Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation on 07/27/2022 in all areas
-
I’m a Muay khao fighter and have been sometimes struggling with sparring. As a fighter I heavily rely on power and aggression to win fights. This is usually because I feel it’s what I have to do in order to win against fighters who are more technical or proficient than me. Almost all the fights I have won were because I was more aggressive than my opponent. Sometimes I have trouble translating that to sparring. You have to be careful with straight knees during sparring, take away the power, etc. Sparring is for timing and technique. I’ve never been the most technical fighter and so sometimes sparring can be frustrating. I’ve seen videos of certain aggressive fighters sparring (Youssef Boughanem for example) and their sparring almost looks totally different than how they would normally fight. I would have loved to see footage of Dieselnoi sparring just because I consider him the greatest. There’s so little footage of him unfortunately online and I always wanted to know what his sparring sessions were like. Would love to know if anyone has received advice before on this kind of struggle. Thank you.1 point
-
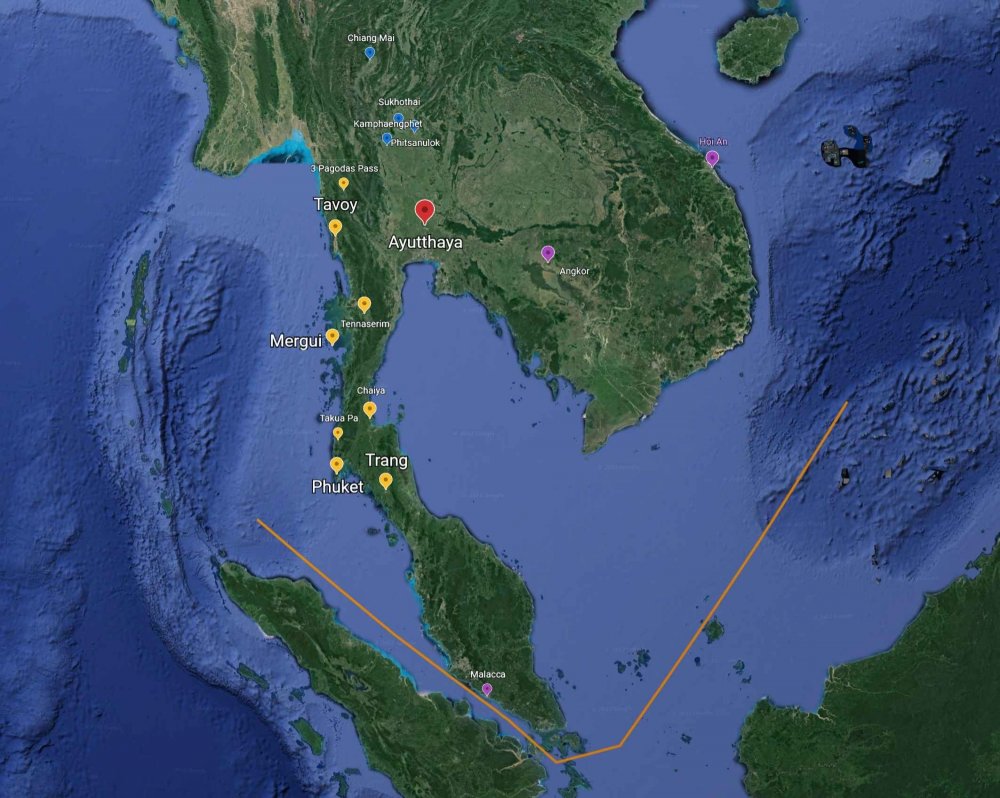
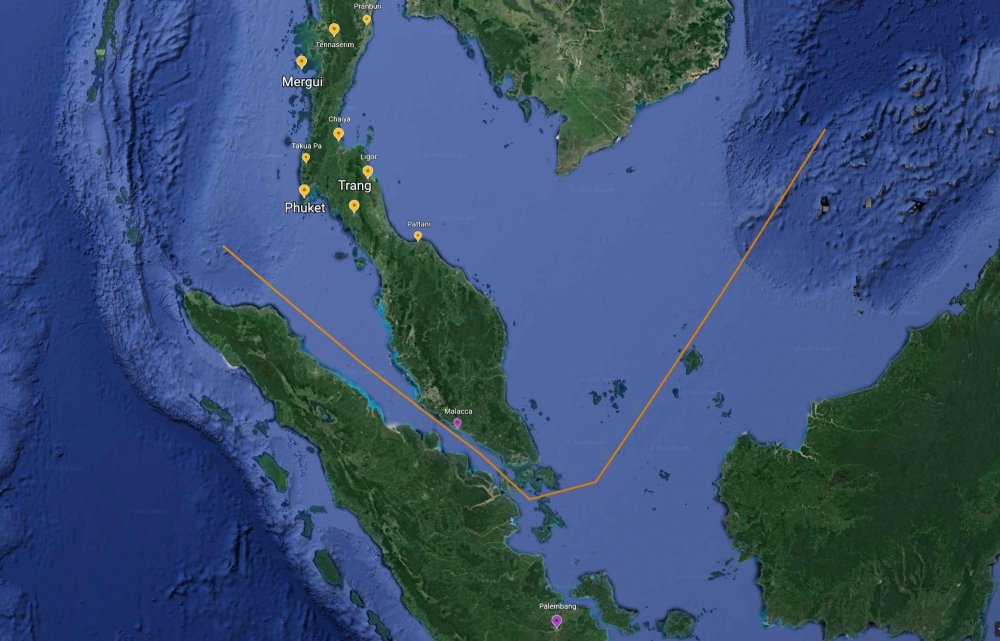
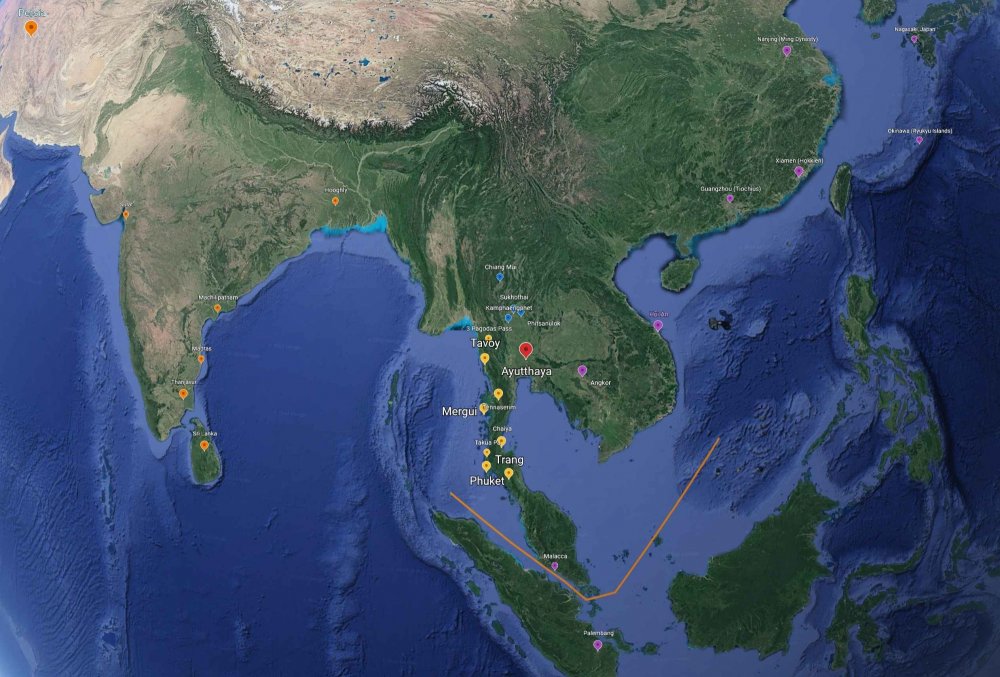
Readings above, a painting of Ayutthaya, Johannes Vinckboons 1662-1663 - Ayutthaya named after the Indian city Ayodhya the legendary capital of the Hindu hero-king Rama. More or less every story of the origin, and therefore really the essence of Muay Thai relates to it developing out of warring Kingdoms, at source coming from the North in very old migrations from Southern China, or from the Khmer in the Northeast. And no doubt these are very strong cultural roots, even its foundation. But, what seems to be left out was the likely possibility it also developed out of the significant and centuries-long engagement with the extensive trade networks reaching as far as China & Japan, Persia and India, not to mention southern powers the present day Indonesian Archipelago. Very likely Muay Boran grew, not only in the context of land-bound warring kingdoms within Siam, it also grew in dialogue and contact with 600 years of mercenary & maritime trade. Perhaps what made Muay Thai (Boran) unique were its battle-field origins, but also its ability to absorb from its cosmopolitan, internationalist influences. A true "mixed" martial art? Below are three really good articles for understanding the nature of the Ayutthaya Kingdom, out of which the history and the mythology of Thailand's Muay Thai is said to have grown. I think there is a tendency, especially in countries of the West which are far removed from Southeast Asian history, to view Ayutthaya, and indeed Thailand itself in a very bound, isolated way. If you've visited the ruins of Ayutthaya, or have seen photographs, it can just feel like an architecture in the landscape. It's 40 miles from the sea. To think about how Muay Thai in its origins may have only derived from warring in the region is to really miss out on what Ayutthaya was. It was an incredibly diverse maritime trading power, with thousands of nationals from all over the world, at one point the largest city in Southeast Asia. Chinese had been there for nearly 500 years. 100s of mercenaries, if not 1,000s from every sea-faring power in residence. In the 1670s the King Narai of Ayutthaya had a personal guard of 200 Indo-Persian warriors. The Kingdom lasted for 400 years. The cultural, cross-pollinating depth of what Ayutthaya must have been, not only in terms of language and ideas, but also in terms of exposure to various fighting techniques and styles, must have been immense. Part of this is understanding that Siam (Thailand) sat atop (North of) a rich archipelago, which along with the Gulf of Siam has been compared to an Asian "Mediterranean Sea", through which ran trade routes from China to Persia. The Gulf of Thailand for 100s upon 100s of years was networked with far-reaching trade. Much of it passed south, around the bottom of the Malaysian peninsula (around modern day Singapore), but there was also a land portage passage, where goods crossed the peninsula to the North. When the Portuguese took control of Malacca, and the Southern passage (1511), this Ayutthaya-controlled land portage path to India & Persia became even more important. Trade had been thriving along this peninsula, what is now Southern Thailand and Northern Malaysia, for more than 1,000 years. I included a map of cities and towns that are mentioned in the reading, just to give a sense of location and distance. What really made Ayutthaya special (and powerful) was the way in which it connected Chinese, Japanese, Malay and Javanese, Persian and Indian peoples to the Northern Kingdoms of Chiang Mai, Lanna, Sukhothai, etc. It was an immense, cosmopolitan melting pot, at one point the largest city in Southeast Asia. That is what Muay Thai grew out of. You should be able to read JSTOR articles with a simple Google login. Ayutthaya Rising: From Land or Sea? (2003) Chris Baker This article takes on the story of how Ayutthaya rose as a Kingdom. Academically, it seems, it was thought to be a land power which harnessed the Kingdoms north of it and then eventually grow toward the sea. Chris Baker argues that Ayutthaya was actually a maritime trading power from its beginning, with very strong connections to Chinese trade (at one point the most documented trading partner of China, in terms of volume). At the confluence of 3 rivers it was a hub of trade that came from the South China Sea, with control reaching down to the Malay peninsula. Only after it grew as a trade power did it become a land power. Ayutthaya and the Indian Ocean in the 17th and 18thCenturies: International Trade, Cosmopolitan Politics, and Transnational Networks (2017) Bhawan Ruangsilp and Pimmanus Wibulsilp This article was fascinating for me, and gives light to just how international a Kingdom Ayutthaya was. It describes the political powers and machinations of Persian officials within the Ayutthayan government. Some of the most powerful men in Ayutthaya were Persians. It's not just a story of fractional politics. It illuminates just how big a role far-reaching Persian trade to the West, across the land portage, played in Ayutthaya's identity. Over these 100s of years there must have been cross-pollination of fighting techniques. "The Sea Common to All": Maritime Frontiers, Port Cities, and Chinese Traders in the Southeast Asian Age of Commerce, ca. 1400-1750 (2010) CRAIG A. LOCKARD This article takes focus on the culture of the Sea upon which the Ayutthaya wealth was partly built. For me it was an essential essay in thinking about just what Ayutthaya was, not only as a political power, but in terms of thinking about the cultural contexts in which Muay Boran (Muay Thai) developed. Along with trade comes warfare, in a broader sense. But also a rich, diverse port city culture presents endless occasions of physical confrontation, in small groups or man-to-man. Mercenary populations abounded. Piracy was a continual concern. A few caps on mercenary use from the above articles: and, (though the million man number is dubious) and,1 point
-
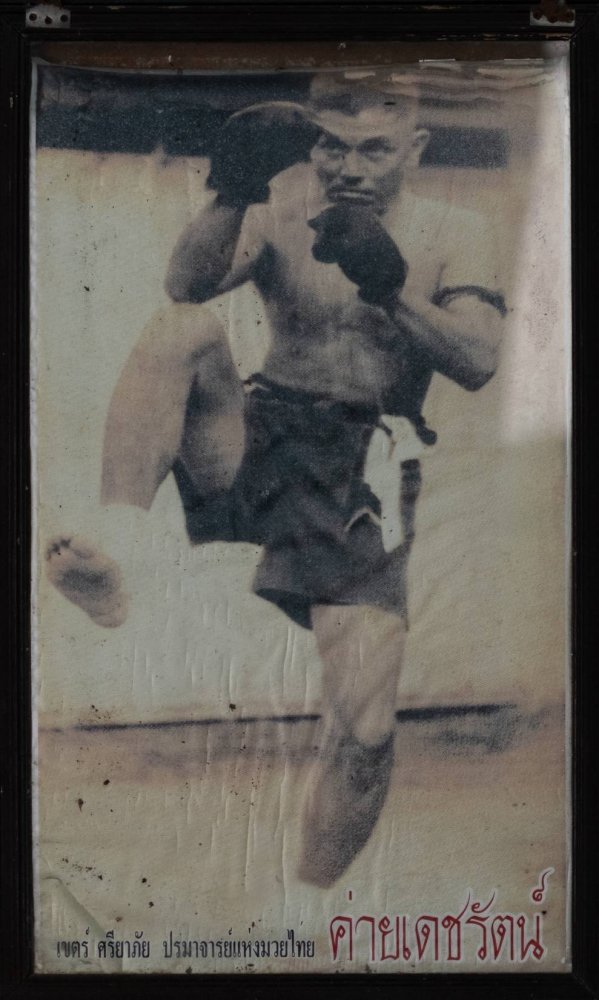
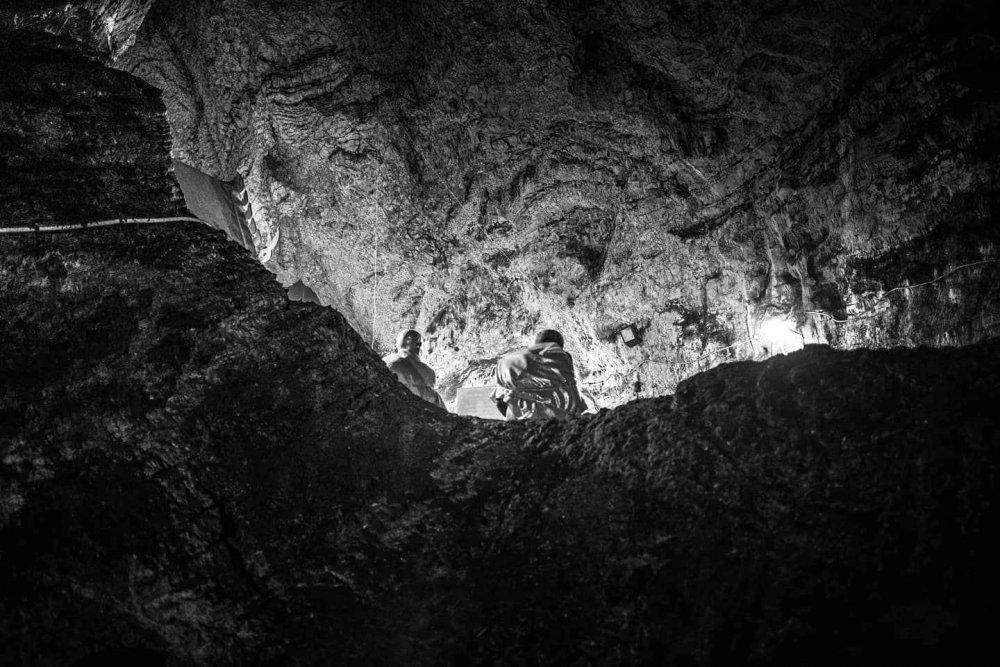
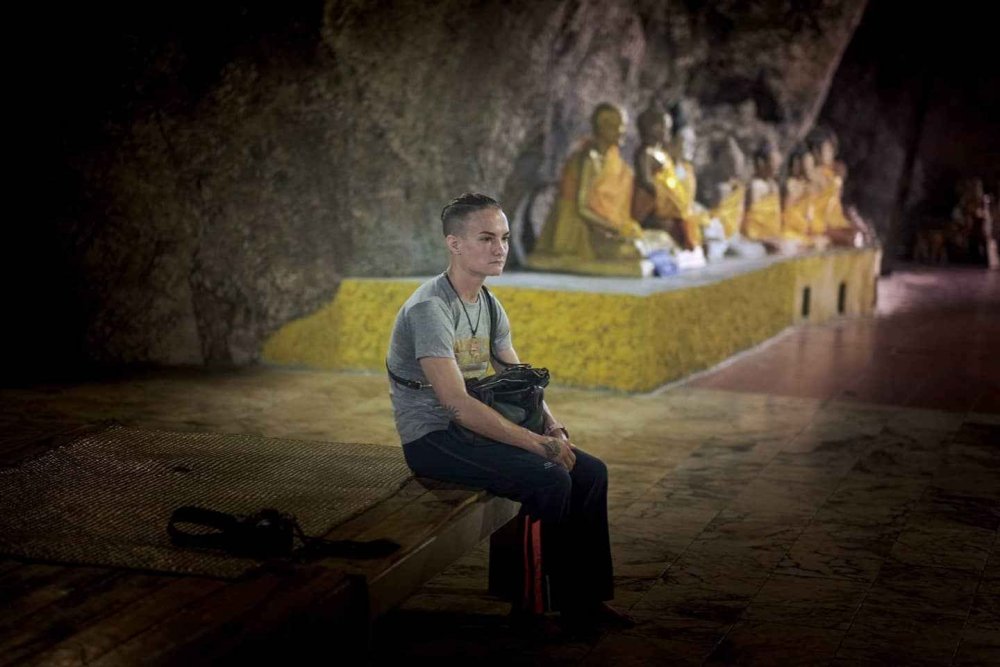
Looking back to Ayutthaya in an attempt to discern individual styles or even techniques, as found in the historical record, runs straight into sheer projection, as there is almost no historical trace of fighting styles of the time. And the effort to ground regional Boran fighting styles with particular teaching lineages is fraught with mythologization and sometimes commercial interests, as if "true" lines of fighting techniques have been preserved and need to be defended through teaching trees for group identity reasons. Muay Boran is an ideologically intense and historically thin area of study and performance, frustrated by how shallow the existing historical roots are. As the legendary Arjan Surat once told us, speaking of the Muay Boran revival in Thailand, pointing to his own Chaiya teacher "If he didn't know, how do they know?" Arjan Surat (who you can study here), unlike many makes very little show about his teacher (below is a portrait he hangs of the training ring), instead he's been training ring-legends for 40 years. Attempting to reconstruct to preserve has its limits. Arjan Surat's Chaiya teacher: Bramajarn Khet Sriyaphai ปรมาจารย์มวย เขตร์ ศรียาภัย But taking up the notion of regional development of distinctive Muay Boran styles, and that there has been a cultural localization that comes from geographic isolation, we recognize the ways in which the geographically isolated Boran of rice-fields and Lao-decedent (Khmer) villages in the Northeast would have had distinctively different influences than say the Boran of the Southern peninsula (Chiaya), amid a littoral culture of trade which had been exposed to Malay, Javan & Indo-Persian (as well as later Chinese influences) for perhaps more than 1,000 years. That's 1,000 years of raid-and-trade culture, in the South. All these peninsula towns of the South were part of the substantial land-portage passage to India and Persia, a bridge between Persia-India and China. You can see Chaiya there. Perhaps more importantly, the entire peninsula was under the control of the 600 year thalassocratic Srivijaya empire (650–1275). You can see Chaiya listed below as a center of Srivijaya power. There is an 8th century Buddhist inscription in Ligor, among the earliest known on the peninsula. You can read a general summary of the Srivijaya empire here: The Srivijaya Empire: trade and culture in the Indian Ocean. It's influence on art, religion (bringing Buddhism and Brahministic practices) for centuries was likely immense on the peninsula. The Chaiya of Muay Chaiya came out of this history, a history of what has been called the "Mediterranean Sea" of the East, which positions the peninsula culture in the pathways of trade (and its warfare) itself, long after the Srivijaya had fallen. The Sukhothai Kingdom (previous to the Ayutthaya Kingdom, and upriver from it), sent as many as a 100 boats to exact tribute on the peninsula in the 1300s. Would it be too far afield to imagine that the very grounded, switching, torso rotations of present day Muay Chaiya dynamics (as taught for instance by Kru Lek in Bangkok) were also amenable to close-quarter maritime fighting, even aboard boats? If we are anchoring fighting styles in their regions, and real fighting contexts, the mixed cultures of port life, littoral culture and international trade as far as India and China, which extends back more than 1,000 years, do seem like candidates for influence. If Buddhism and temple architecture can be brought by a sea empire, one assumes that real-world fighting techniques also would cross-pollinate. While there is no direct connection of Srivijaya fighting techniques and Siam Southern styles, quite common and sought after in the 19th and early 20th centuries were practices in (religious) Magical arts. These were Brahman yants, rituals and potions said to imbue a fighter with impervious skin. Bandits and local chieftain authorities regarded these as essential fighting powers. These were reported of the Srivijaya warriors nearly 700 years before (in the year 1178, cited above source here). These practices were famous in the Wat Khao Aor in the South (Phatthalung), a historic center of the wicca of fighting magic built around a sacred cave thought to have been a place of worship for 1,000 years. It is not a stretch to imagine that these magical warfare practices, in part, came from the Srivijaya era and influence (Vajrayana Buddhism), woven together with Buddhism and Brahmanism that also was spread through the sea-faring Empire, distinct from the saiyasat magical practices of the Khmer Empire to the Northeast. (For more on the unique Brahman religious history of the mid-South.) If techniques of magical warfare practice can be transmitted, so too could fighting techniques and styles. You can read more about these magical practices in the biography of the famed early 20th century Southern policeman Khun Phantharakratchadet (1898–2006) (see the link at the bottom of this post). These are my photos of Wat Khao Aor, a kind of 19th century southern "Vedic" Magical University in terms of the fighting arts, still a very sacred place. On Khun Phantharakratchadet (1898–2006): read it online here Also as part of this thread:1 point
-
a link to my map on Google Earth - in this graphic you can see the southern Siamese portage peninsula cities (yellow), the northern Siamese kingdoms (blue), western Indo-Persian trade centers (orange, to the left), the Malay archipelago cities (bottom, purple), and the eastern city centers on the way to China (purple left). It gives a sense of how vast the reach of cultures was in the Kingdom of Ayutthaya. You need to read the articles in the first post to specify it. In many respects this is about how to deal with historical fable. In saying that the lore of Muay Thai history is composed of fable does nothing to minimize it. In fact the stories of the roots of the art and sport go a long way towards orienting ourselves to its value, and in Thailand how Muay Thai is anchored can be of extreme importance. Peter Vail's article on the National symbology of Muay Thai is a good discussion of this: Muay Thai – Inventing Tradition for a National Symbol – Peter Vail PDF (full article) For me, as a Westerner coming to Thailand's Muay Thai I did so with a degree of naivete. Only very broad, perhaps exoticized pictures of the antiquity of the art, home-grown in the wars and battles of a faraway land - battle tested if you will - populated my conception. Visiting the ruins of Ayutthaya, or even seeing the brick reconstructed walls of Chiang Mai's inner city only gave more reality to what really were fable-istic ideas of Siam history. But, what persisted through it all was the idea that Muay Thai (and its Muay Boran antecedents) where uniquely Thai, and had developed in something of a cultural test tube, cut off from the outside world. This involved very broad notions that even things like Western Boxing were not really known to Muay Thai until fairly recently, or the idea that when Westerners came to fight in Thailand in the 1980s and 1990s this was some sort of breaking of the seal, on an otherwise closed evolution of the fighting art. Or the idea that today's pressures for Muay Thai to change under Western and globalized commodified forms were the first real radical disturbances of what Muay Thai was. Forgive the simplicity of these pictures. I do feel they are fairly common for people unconnected to a culture that is not their own. As I read I came into contact with theories of Muay Thai's origin in migrations from the North, and the similarities that are found in Myanmar (Burma), Cambodia (Khmer) and Laos. But Thailand's Muay Thai held a certain distinctness, a kind of bold relief, that seemed to cut it out away from those lineage connections. And, I was always aware that when other, culturally competing countries proclaimed their originality of Thailand's Muay Thai there was always a sort of ideologically game going on. They nearly always contain a kind of "Who's your daddy?" rhetorical force which is Asian culture is substantial. Finding and revering the root of something is of great importance, in terms of its meaning. That being said, the Kingdom of Ayutthaya features prominently in anchoring the very Thai-ness of Muay Thai's history. It was a rich, long standing Kingdom of much renown, and when the Chakri Dynasty founded itself in the new capital of Bangkok it took great care to actually build the royal edifices out of the very bricks and materials of fallen Ayutthaya. The name "Ayutthaya" was even put in the formal name of Bangkok itself. Bangkok was a New Ayutthaya, the unbroken lineage to Ayutthaya was extremely important. And even today there are Muay Thai/Muay Boran celebrations in the city of Ayutthaya on Muay Thai day. Ayutthaya is the ballast which allows the Muay Thai ship to sail, historically and ideologically speaking. It was for this reason why reading these essays were eye-opening for me. They pealed back the photos of the ruins of Ayutthaya and opened a window into just what Ayutthaya was. I've read them several times, pulling from them the brief first-person descriptions, and authorial summations which made Ayutthaya vivid. It was very different than anything I had half-conjured in my mind in the first years of my love for Muay Thai and living in Thailand. Instead of august ruins and fallen temples I saw a rich port city that was home to an incredible array of the worlds cultures. It was called "The Venice of the East" in its time, and like powerful trading ports presented a confluence of influences. And...importantly did so for 100s of years, longer than the existence of my own country the United States. If Ayutthaya in some way - symbolically, ideologically, and culturally - anchored what Muay Thai was, this was quite an anchor. Japanese mercenaries and pirates who brought their own fighting styles, fought along side Siamese warriors, and lived in the city for centuries came in contact with 1,000s Chinese junk traders and their families, who also lived in the city, in their own quarters. Indo-Persian troops who guarded the King in the 17th century, with their own warfare styles, no doubt in contact with Siamese fighters. And this is just in terms of martial events such as raiding, warring, suppressing pirates, exacting tributes, in which company was no doubt mixed. If one draws to mind the realities of what port-city life is like: gambling districts, gang crime, syndicates, drinking houses over 100s of years there must have been group on group, man on man agonism, where fighting techniques played out against each other. Even if peoples kept to their own kind in a highly structured society - and we know there were quarters for every culture - over centuries the cross-pollination in lived struggle, in back alleys and on docks had to have a certain cumulative effect of knowledge sharing. Even in the most ideologically restrained contexts when actual fighting is happening, what works is what is valued. Whether this is in raiding parties or in settling unpaid gambling debts there is little room for show. What is fascinating is that Muay Boran (Muay Thai) grew in part out of this melting pot of fighting style reality, the actual docks and floating gambling houses, as well as mercenary-enriched martial battles and skirmishes, but also retained its distinctness, and regional character. I suspect that this is something that Muay Thai (and perhaps even Siamese / Thailand) possessed, the ability to always incorporate the foreign, but to quite strongly mold it back into a very Siamese identity. To make it its own. To absorb and revalue. It does not really copy. It integrates. When Muay Boran was ostensibly "created", that is to say officially recognized by King Chulalongkorn in 1909-1910, and demarcated into 4 regional types, it actually was on it way out, so to speak. The recognition of the art was at the historical precipice of its modernity. By 1928 gloved fighting would become mandatory and Muay Thai would be reborn in the image of British Boxing, with weight classes, padded and roped rings, and fixed stadia. You can see a timeline of these events here. It was a time of a great modernization (and Westernization) of Bangkok as a cosmopolitan city of the world. In the year 1900 there were 3,000 British nationals working in the Bangkok police force. When you read about the modernizing years of 1900-1932, under the dialogue with the culture of foreign Nations from far across the world, and you read about the great trading power of the cosmopolitan city of Ayutthaya, you realize that this wasn't the first time for such a cross-pollination. New Ayutthaya was in the model of Old Ayutthaya, at the center of a great confluence of culture. There can be no doubt that in Muay Thai's history there are distinct regional styles of Muay Boran that grew out of geographic isolation. Muay Khorat (from the Northeast) was different than Muay Chaiya (from the south), and it is a suspicion that it was the building of railroad lines connecting Bangkok to Khorat (1900), the South (1907), Lampang (1916) and Chiangmai (1921) that produced an enormous flowering in Muay Thai, as styles that grew regionally, in 1,000s of festival fights came in contact with each other in the new rings and then stadia of Bangkok. Part of what is beautiful about Muay Thai, even today's Muay Thai, is that it has grown out of regional branches, branches of which experienced relative independent growth and stabilization within the cultures and customs of that province, and that these branches have periodically been brought together at various times and ways in history. The building of the railroads in the early part of the 20th century and the formalizing of the sport in the early part of the 20th century was one, the great economic boom of the 1980s and 1990s, and promotional Muay Thai of the Golden Age, another. These regionalizations of Muay Thai I believe were very important to its distinctive and rich character, the times that it did develop in isolation, in niches, in festivals. It gives it great particularity and definition. But, I think what the character of the Ayutthaya Kingdom also tells us is that these distinctive isolations also, for centuries upon centuries came in contact with other modes of warfare, other fighting styles, not in terms of adversaries (though that is no-doubt true), but in terms of cohabitation and mercenary/martial mixing. It is likely just an incredible mixed and mixing martial art. And has been for maybe 800 years.1 point
-
Stay super playful durring sparring sessions. Work on integrating defence moves that get you inside and in positions where (if you were in a fight) your muay kao style would benefit, and then smile at your partner and reset (thus your muscles are learning without finalizing the action). Another great sparring goal is to find yourself back at center and cutting off partners movements. This helps when you start going too hard.1 point
-
One thing that I find its important to remember is that sparring is all about learning not winning as much as it sucks to feel that your opponent got the better of you. Sounds like you are already good at being aggressive so its worth working on the the things you are worse at during sparring. I find the best thing I can do when sparring is have a goal. I want to work on my Teep/Headmovment/range and make that my primary goal. Don't only do that but it allows you to have something you can focus on even if you are outhit. "Yeah the other person hit me more but I can feel my teep improving" is a good feeling and very worthwhile.1 point
-
I've likened my experience with this kind of thing as being like having a wife and a mistress. They know about each other, but you'd better not f***ing talk about each of them to the other one!1 point
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.