-
Posts
2,281 -
Joined
-
Days Won
503
Everything posted by Kevin von Duuglas-Ittu
-
If I have swept out too far in theory or even in example, let me bring it back down to basics. What does it mean when a Westerner is told "Now do 500 knees on the bag"? And, he does them in synchrony with Thai boys in the gym who may (or may not) be contracted to the gym, and held by invisible hierarchical strings the Westerner cannot see? He/she is participating in a form-of-life when synchronizing himself/herself to the command and its performance. The bodies literally synchronize up into a rhythm, and the longer and more devoted he/she is, the more thorough the synchronization, not only in body but in spirit. What does it mean to do those knees? Are they doing them in the same way? Under the same motivations? Or, is the question: Are they undergoing similar transformations? As a Westerner syncs up not only on the bag, but to the other rules of the space: where and when one sits, or drinks, body postures when resting, the timetables of practice and signatures of effort, deference, suffering, the human sharing of the body under rule creates a sympathy of experience, and because rule-governed an authenticity, the collapsing of representation and action. With some complexity, if not outright irony, Agamben compares the temporal rigors of the 13th century monastery to what is otherwise assumed to be prototypical modernity, the assembly line of Ford and Taylor:
-
The philosopher and critical theorist Georgio Agamben writes a curious book examining in arcane detail the debates and legal disputes surrounding the Franciscan order around the 13th century. In The Highest Poverty; Monastic Rules and the Form of Life he takes on the more-than-century-long wave of monasticism which sought to strip itself of "property" and to live a life, what Agamben importantly comes to single out as a form-of-life, in imitation of the life of Christ and the apostles, a life of the Highest Poverty. What he traces is how this form-of-life ambition and practice, as it grew, came to threaten the authority of the Church it was under, and how the struggle for power and autonomy between them played out in arguments over just what "property" was. Why does he take on such a historically obtuse subject matter? He feels that somehow this legal and intellectual dispute over what "property" is, and the way in which the Franciscan order organized itself - hermetically - in a rule-governed, highly disciplined way of life, in which practically ever hour of the day was performatively accounted for in prayer, liturgy recitation, readings, worships, silences, actually presages contemporary attempts to free oneself from the alienations and power of Capitalism. Just as Fransiscans sought to hollow out a living space under the Universality of the Church, a rule-governed poverty of sacredness in pursuit of making of their lives a form-of-life, so too might contemporary humanity relieve itself of the defining authority of Capitalism and its experiences of alienation. He is pursuing a certain logic of rule-governed life and examining the ways in which it may seal oneself off, or, return one to a more human mode of existence, and he uses the disputes over what "property" is as an intellectual wedge to explore this. What comes to me in the reading is actually the way in which the traditional Thai kaimuay (Muay Thai camp) and the Thai Muay Thai gym (here, gym spaces which are structurally open to westerners and non-Thais) actually embody something of this logic of the cloistered rule-governed space, and how the rigorousness of physical, mental and (even) spiritual practice in the kaimuays and gyms does in some way reflect this division of power, authority and meaning that Agamben is invoking across the centuries. I mean this perhaps in two ways, or from two directions. The first is the way in which the traditional Thai kaimuay itself is woven from pre-Capitalist social forms (to be very broad about it, Feudal relations of patronage and hierarchy), so that the kaimuay for Thais very well might be a place of counter-Capitalist meaning making; and the second is that as those spaces and practices have come to be structurally open to traveling westerners and non-Thais an attraction of those spaces and practices is the very relief they give to the Capitalist worldview which is over-permeated with representations and simulations of living. This is the say, just as Franciscans retreated from the ubiquity of Church practices to find an authenticity of living, to make of their lives a physical, temporal and spiritual reality which was what it was doing (collapsing representation onto practice itself), stays and various devotions to Thai gyms also are this kind of reach for authenticity and transformation. What is key here, is that this may hold no matter the degree to which one makes this commitment, whether it is a traincation where you play at the beach and then do some padwork, or if you journey to an Isaan kaimuay where English is not spoken and you sleep on the floor with the Thai boys. The pull is towards an authenticity, and importantly people are having experiences of authenticity in a vast array. Here Agamben talks about how the Franciscan order disciplined life to the degree that monks became "living clocks": I think for many who have come and devoted time to the kaimuay and Muay Thai gym experience the question of authenticity becomes a primary one. There is perhaps a tendency to judge the (less committed) authenticity of others, and also to fear that your own authenticity might be judged, much as perhaps happens in let's say Buddhist meditation retreats or even yoga practices. One can always do more, be more committed, or rule-governed, more immersed, by degrees. Significantly though its best to see that more or less everyone is having authenticity experiences, and these come from the isolating, rule-governed, physically and emotionally demanding practices, the way in which the kaimuay and the gym segment off life in a structured expression. For any who are feeling that the comparison of the Muay Thai gym to a Buddhist retreat or temple is a stretch, in Thailand sociologically and historically there is actually great overlap. From the Thai perspective the idealized masculinity of the Nak Muay shares many qualities of that of a monk: read up on this here, Thai Masculinity: Positioning Nak Muay Between Monkhood and Nak Leng – Peter Vail, in fact the custom by which boys are brought to a wat to become novice monks (to earn karmic merit for their families) and may be brought to a kaimuay (to earn financial support and perhaps esteem for their families) are not too dissimilar. They involve a form of adoption into a highly regimented and challenging way of life, a form of labor which is meant to produce value and surplus. Both historically have been social practices which involve the inculcation and self-fashioning of an idealized masculinity, in a cloistered world. And both are pre-Capitalist in their formation. There has been a kind of fighting spirituality in the Thai kaimuay, historically. What is Use, What is Property? Key to Agamben's argument is how one thinks about use and property. What Franciscans sought was to live a life without property, a kind of holy poverty. In their attempt to define what they meant about use and property they appealed to the kind of use of things that animals have in the world, or children have in a family. Animals and children eat freely food, make use of the land because in a certain sense they are part of a Commons. A commons is a realm of resources to which everyone has access to, according to need. The fact of their need composes their right to use it. One can see rather quickly how this can escalate into utopian ideas about sharing and distribution, but, what is more important here is to keep an eye on the very rule-governed nature of how these commons are created. Agamben wants to argue that following rules is very different than following laws. Rules are a way of doing things. Yes, there are consequences if you break rules, and rules may not be entirely written out, but they categorically not like laws. Laws create divisions like "criminal" or "citizen". Rules are ways-of-life. And this goes into the ways in which a 13th century monastery (or a kaimuay) fashions a living experience which (ideally) does not separate itself out from its representation. One enacts what one is supposed to be, and does so in a highly heirarchized way of life. For westerners, because they largely do not speak or feel Thai, they do not read the hierarchies in these spaces. The orders which organize the life of the gym for Thais largely remain invisible to them. Instead though, they do experience the commons of a practice, of the living fight space, and they do experience the orders of training and some of its rite and ritual. And these are often experiences of authenticity, a respite from the copious simulacrum of Capitalist representations which otherwise organize a westerner's life (taking just for an example, social media representation, a recent layer upon many layers of representative, simulacrum life). Here is Agamben on how all of our (Capitalist) lives have been turned into almost tours of museums, walking through things that no longer are, representations of what is Real, with the note on the rise of tourism. Ironically enough, tourism is a powerful factor in western visits to Thailand, and the Adventure Tourism of fight training and actual fighting plays a significant role in this: This is where the question of tourism and the thirst for authenticity braid. There is a certain sense of Adventure Tourism in the Thailand Muay Thai experience, that westerners want to experience something exotic, and in that way unlike their own lives back "home". But I think as well, they are also drawn to the pre-Capitalist creation of a commons, and the rule-governed experiences of use, as they reach for a way-of-life, wherein representations are collapsed into the Real of what one is. These now, as as they are visited and submitted to, are hybrid spaces. They embody pre-Capitalist forms of life and practices of transformation, but they are also Capitalist businesses ripe with representations and commodification. And the flux of westerners, with their own blend of motivations spectrumed from the tourist to the cenobian, further hybridizes these spaces. There is no clean, clear view of exactly what is happening in them, as each is its own experiment and variation.
-
It seems unrealistic to look for gyms like there were 30 years ago, and Jocky was pretty unique even in its day. Most likely it would be best to just find someone you would like to train with or under, and take privates from them. Samart has his own gym in Bangkok (in the north of it) and I believe he teaches privates there: https://web.facebook.com/samartpayakaroongym
-
Gym recommendation technique and teaching
Kevin von Duuglas-Ittu replied to TRTdoc's topic in Gym Advice and Experiences
I'd consider going to Thailand Pinsinchai's gym in Chiang Mai, and taking privates from him as well. He's very technical, an excellent instructor, and the gym itself is a living family run gym with Thai fighters. The gym's FB page is here: https://web.facebook.com/Sit-Thailand-Muay-Thai-Gym-106840670828643 You can see two privates with him in the Muay Thai Library, just to get the sense of his teaching style. It strikes me as the perfect balance between authentic gym and lots of technical instruction (if you take privates from him). -
Some comments on Reddit on this post reveal that I was far too opaque about the idea that it is worthwhile to see Muay Thai as a language. I probably lost a lot of people who might find it interesting. Sometimes I'm far to oblique in my thoughts, and these forum posts are often just publicly published reading notes of areas I'm diving into in my reading, just in case others might one day also want to follow these lines of thought. But...in the course of my discussion there I was lead to explain further what I meant by "Muay Thai is like a language". I also got an awesome reply. Posting it here to keep it in context and to keep it from being lost on the Internet. My take on Muay Thai as a language and why I view it that way: My general thought about Thailand's Muay Thai and language is that it is an embedded art, which means its very difficult to extract the techniques in a bio-mechanical way (which is the dominant way it is exported to the West). Much of Thailand's Muay Thai is a product of the kaimuay subculture, the culture bound practices of the camps that raise the fighters, going well beyond simple techniques. These have to do with bodily disposition, relationships to authority, cultural attitudes towards aggression and discipline, and ideals of Thai masculinity. Which is to say that Thailand's Muay Thai is shaped by the Form of Life of the kaimuay, of which there are thousands and thousands in the country. The benefits of reading Thailand's Muay Thai as a language are that its an analogy that directs the idea towards things like a "grammar" (the way that strikes are put together, in relationship to bodily composure), and to the kinds of things we think about when we think about linguistic expression. In Thailand's Muay Thai a great deal can be read in the way that strikes are expressed, just like the tonation of words, and choice of words reflect a great deal in speech. At least in my opinion, there is an entire meaning universe in these kinds of things in Thailand's traditional Muay Thai, that in the muay of the very best become personal expression. This, in part, is why styles were so varied in the Golden Age. The grammars and vocabularies were being combined with great individuality...like a language. Dropping back down into the subject of the post, how Muay Thai strikes can be read as words, with "accents", at least by my experience of watching legends spar and move (for instance, I've spent maybe 50 hours closely watching Karuhat spar), as well as many contemporary Thais, Thailand's Muay Thai has a kind of acceleration towards the end of strikes that you don't really see in many Western kickboxing-like examples. It's a feeling of the word. It happens to coincide with the way that Thai language borrows English words and changes the pronunciation of them, putting the accent on the end. When you come to Thailand you have to learn that "com-PUT-ter" is actually "com-put-TER". It makes a nice cross-reference. This movement from relaxation to acceleration is - at least in my view - a really distinct aspect of the shape of Thai striking. Sorry that it isn't really a summation, it's not really how my brain works, but its an attempt to try to clear up some of the larger ideas behind the "Muay Thai is like a language" analogy. Ultimately, its not really about being right, but rather about trying to present a different way of thinking about strikes, something that departs from the usual bio-mechanical way of thinking about striking. There is plenty of that out there. This is just a new framework to change the perspective a bit. Something to add to the bio-mechanical story. Personally, I find it fascinating how Thailand's Muay Thai might resist exportation outside of the kaimuay subculture which generates it. It draws attention to all sorts of things that might just get silenced or minimized. Again and again in my mind I recall how Dieselnoi insisted that there was a very important way that you come off of pads. There is a way it needs to be done - in his opinion. There is a disposition of the body, a way of presenting yourself and shaking off exhaustion. This at first blush seems to have nothing to do with striking mechanics. But, it is an expression of the long-closed-down Hapalang Gym of the Golden Age. It's HOW he trained. It's part of the language of Muay Thai for him. And...if you look at his relentless, GOAT-like knee style, this way of coming off the pads actually is a huge part of his fighting style. I'm interested in all those things, the non-obvious parts of Muay Thai that are embedded (or were embedded) in the kaimuay which generated the muay of great fighters. If one grants this, then learning how to pronounce individual words, in this language, is an important place to start. The awesome reply, which is full of application eatmygorts TL; DR: Totally agree that muay is an embedded art that makes very little sense outside of its cultural context. I think your analogy with language is also spot on. I think an additional challenge for spreading the art, and this is something I haven't quite fleshed out in my own mind, is that Westerners (not all, but in general), culturally, have a very transactional and (edit) mystical mindset about this sport and the fighting arts in general. I have observed similar parallels with non-indigenous folks learning an indigenous language that is also deeply embedded in cultural context, so it's not just a issue in muay. Longer answer: Oh cool, thanks man! Normally I wouldn't ask for a summary of the source material, that's kinda lazy, but I just wasn't getting it, and neither were other people. I actually really like this analogy. Thinking about it this way makes it easier to understand why people have such a hard time learning Thai style muay, to a level of fluency that appears "native". The only people that I know personally that have cracked this are those that have emersed themselves in a Thai Gym for an extended period of time, speak at least some Thai, and understand intrinsically the fight scene in Thailand. I think this analogy also makes sense from your perspective, as people trying to preserve the old "language" and context that gave rise to that, as it evolves. This is a bit of a take, so hear me out. In my country, there is a lot of effort going into language revival of our indigenous language, that was effectively stamped out through colonisation. The language is utterly beautiful when spoken fluently - a confluence of past and present that is embedded in a strong oral tradition. It is simply much, much more than just a means to communicate to one another. I bring this up because I find that a lot of non-indigenous people, when looking to learn the language, do so to "acquire" the language and generally want to skip all the "cultural stuff". They see the language as merely a tool, nothing more, missing the bigger context and cultural relevance. It's generally well meaning, mostly, but still problematic. So I've often noticed that people in my country/the West (generally speaking) look at the Thais as quite alien and Thai muay as something (edit) mystical. Like, they see that the Thais are good, great even, but don't fundamentally understand what makes them good. They go about trying to acquire their techniques, without the context of where and how they are used, and not understanding the process that has led them to be so effective. Basically, acquiring the language without any context, picking up words here and there (emphasising different syllables, if you will), but developing no real understanding. They're missing the wood for the trees. Or, like my example above, maybe they do know there is more, but they don't see how it's relevant to them. They don't want to walk the path of countless Thai fighters before, even on a very basic level, like running. They don't think they need all that extra stuff, just learn a few techniques and some technical sparring to be "good", for a Westerner, because they have no actual aspirations to be like the Thais. This is reserved for some next level of "fluency" that they believe is unattainable for the average Westerner. Edit: Some stuff you can't replicate easily, if at all, because of those deep cultural roots that start at childhood. But even if people are given a blueprint of what it takes to be good - how to train, what it takes, where to go, who to train with - 9/10 they won't or can't do it, because they don't want to put in the work. They don't connect to the process at all, or it's importance, and want a simplified version of it. I did watch one of Sylvie's little videos a while back on the "hack" and I think this touches on aspects of this. Anyway, just some off-hand thoughts here. Edit: I guess one of the challenges that you and Sylvie have is that by producing the content you do, even if it is really good, interesting and contextual stuff, is that people are still going to see it as a collection of techniques to acquire, to be like the golden era, or what have you. You can't really control how people use your material, or how they approach the learning process, and that unfortunately has a big impact on the transference of Thai style muay abroad
-
Old school muay thai coaches in Chiang Mai
Kevin von Duuglas-Ittu replied to Dmian's topic in Gym Advice and Experiences
This is an old link. Kru Thailand used to be at Santai, but he left to open up his own gym a couple of years ago now. I think also the Santai head trainer Kru Apple did as well. -
Old school muay thai coaches in Chiang Mai
Kevin von Duuglas-Ittu replied to Dmian's topic in Gym Advice and Experiences
You can find the gym's FB page here: https://web.facebook.com/Sit-Thailand-Muay-Thai-Gym-106840670828643 You can get a feel for it from the photos and videos posted. Also Sylvie has filmed with Kru Thailand 2x for the Muay Thai Library if you want to get a feeling for his teaching style: #83 Thailand Pinsinchai 2 - The Beauty of Clinch (57 min) watch it here In Kru Thailand's first session in the Library he taught all the principles of his femeu style, in this session, his second in the Library, he breaks down all the things necessary for his dominant clinch attack. Spend an hour learning the techniques that make clinch turns and damaging knees possible. All of it is balance and rhythm at close range. #16 Thailand Pinsinchai 1 - Attacking Shell (62 min) watch it here Former Lumpinee and Rajadamnern champion Thailand Pinsinchai teaches the beautiful framework for his attacking, elbowing style. Lots of minute corrections, small vital details that turn working techniques into dominance. You get the entire picture of a Muay Buek fighter out of the legendary Pinsinchai gym . -
Ah yes. I forgot to get a bit into another way in which fighters seek to overcome surprisal, which is neither the shrinking of the probability space, nor the complexified growth of predictive awareness. This is the use of memorized combination patterns of attack. This is often a bite-down approach to the probability space wherein one inures oneself to surprise itself. It does not matter if something unexpected happens. One just tunnel-visions and locks into a very rehearsed and trusted somatic pattern of attack, designed to (hopefully) produce favorable outcomes regardless of opponent/environment. This is locking oneself into a closed form. An interesting historical occasion of this in the history of Muay Thai was when Namkabuan at the end of his career fought Ramon Dekkers who founded much of his fighting style on memorized combination fighting, Namkabuan's commentary on the fight here. There are also more restricted versions of this kind of bite-down approach to surprisal, for instance the insensate use of some kinds of guards, in which surprisal is just weathered through.
-
Cliffnotes summation: Muay Khao fighting style: 1. Shrinks the probability space (closes physical distance, limits weapons). 2. Changes the dominant affect register (from visual to tactile/kinesthetic). 3. Through its ars technica increases the probability space (learned/discovered dynamics of movement & control).
-
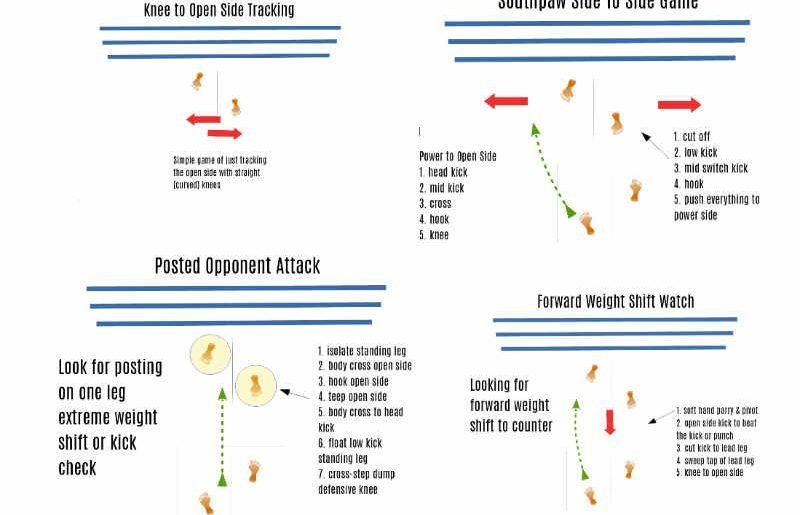
What follows is intersectional thought between an increasingly robust philosophical and scientific theory of living systems, and the art of fighting in combat sports. If you want to stay on top of the Free Energy Principle theory Maxwell Ramstead on Twitter is a great place to start. For me, personally, in the Free Energy Principle I find a lot of correspondence between itself and the philosophy of Spinoza, and it has always been my instinct that Spinoza has important things to say about some of our most concrete interactions as people. In some sense fighting is one of the most attenuated, physical yet social things that humans can do. This is about looking into the heart of what makes living systems tick, the possible dynamics which give all living things their values and their direction. And it is about thinking on the deeper metaphysical and scientific foundations of fight knowledge, the practical application of techniques and styles that have developed over the last century in Thailand. In bringing the Free Energy Principle to Muay Thai it is much more than a somewhat trite adage of: try to surprise your opponent! It is much more about thinking how surprise governs our choices of space, and the investments we make in maintaining those choices. And it is about recharacterizing the fundamental ways in which fight strategies and their tactics, create success. If organisms are at base in a struggle to control the entropy of information, increasing that entropy, taxing the resources of a fighters, is essential to long term fight success. I don't anticipate that this is for everyone or even most; this is just my passion where Philosophy and Fighting co-exist. As usual to my writing, this is not a finished article, but rather the sharing, mid-stream, the development of thought. The Free Energy Principle Theory Editing in the very best introduction to these ideas "An Introduction to Markov Blankets and Information Theory". Read this if you want to full, yet basic perspective. and from "Brain Entropy During Aging Through a Free Energy Principle Approach" (2021, below: This rumination will flow from the Free Energy Principle (FEP) which seeks to describe essential characteristics of living systems (being) and perhaps other phenomena as well. If you'd like a great 15 minute introduction to the principle you can check out this video explanation by Karl Friston. The Free Energy Principle generally argues that life forms, human beings included, benefit from reducing what in theory is called "surprisal" ("One can understand surprisal as a measure of how unlikely an observation would be by associating a system's sensory state with an observation or sensory sample"). Surprisal is here maybe best taken as just the surprise of events in the environment which are unpredicted...or unpredictable. This framework of reducing suprisal actually has very interesting broad brush insight into stylistic and skill-set developments in Muay Thai (and all other kinds of fighting arts). If we take as a principle in fighting the desire to reduce surprisal, there are two basic ways to do so that come at first blush. The first is the reduce the size of the probability space, which is to say limit the number of things that can possibly happen. By shrinking the probability space the number of possible unexpected events becomes reduced. At a very basic level, this is why octopi retreat into coral enclaves to sleep. The probability space becomes reduced (I'm using this term perhaps untechnically, it perhaps could be called the "event space"). This also is why people live lives in more rigidly defined circumstances, whether that involves habits of behavior or the habits of mind which condition them. Reducing the probability space can control surprisal. Reducing the probability space though has its drawbacks. You may not be able to control that space. This leads to the much more fruitful - though expensive - method of controlling surprisal, which is complexifying the prediction mechanism (the brain, nervous system, etc) so that it can predict events in larger probability spaces. More varied things can happen, and the mind (& body) is able through its development to read those patterns and become less able to be surprised. The richness of embodied knowledge over a probability space involves a mastery over it. And this process of complexification actually feeds on surprisal, because surprise causes it to grow in terms of complexification. The more unaccountable things it can account for, the greater its knowledge over a space. The Free Energy Principle, Surprisal and Fighting This leads to the tale of Sylvie's early year experiences of fighting in Thailand. She fought at an intense, never before documented, historic rate having over 33 fights a year for several years, but she was facing a serious disadvantage in these years. She was fighting more experienced opponents, with better eyes, who were much more familiar with the scoring aesthetics of Thailand. These Thai opponents had a very significant advantage in terms of surprisal in the fight space. Sylvie's stylistic solution to this was her discovery of the Muay Khao fight style tradition (a close-pressed, stalking fighting style that capitalized on clinch and knee fighting). She was aided in this in the discovery that there was in Thailand's history a traditional opposition between Muay Femeu (artistic, technical, often counter fighting) and Muay Khao fighting. This is where things become interesting. Muay Khao and Probability Faced with a disadvantage of fighting in a larger probability fight space, and not having the eyes and experience to read those probabilities visually, Muay Khao fighting tactics seek to shrink the probability space. In fighting close pressed, closing down angles, limiting distances the number of possibles to account for became more limited. It leveled the playing field more. But it is more than this. It also changed the dynamics of fighting and perception skills at play. In a more "padwork distance" fight space (fighters standing at basically the distance where training pad work is done) visual acuity reigns, but in more close range, clinch-oriented fighting tactile sensing can become paramount. By developing other sensory pathways (other than just eyes), and specific techniques to use them (locks, trips, turns, leverages) this new, (seemingly) smaller probability space then became expanded. Expanded in a different sense: what is possible in terms of historical skill development. The entire art of Muay Khao fighting actually is about expanding the possibilities of what can happen, at close range, exposing your opponent to increased surprisal. What began as a strategic shrinking of the probability space lead to the complexification of the art within that space, through both an inordinate number of fights (now well over 260), but also through the study of the art of Muay Khao fighting itself, and the richness of its specialized tactical knowledge. An example of a recent development of this tactical knowledge, anecdotally, is Sylvie's discovery and development of clinch throws from an outside position. Usually the preferred position in clinch is with an inside frame (Sylvie talks about the frame here). This where you are able to control the body of your opponent most directly, framing them. But through lots of sparring with larger partners Sylvie has spent a lot of time over the last few years in an outside (inferior) position. From this position, though technically inferior in important ways, one gains a dynamic advantage of some leveraged turns, trips and throws, introducing more centrifugal rotations to otherwise very erect, linear opponents (standing erect or stiffening can be a principle of strong clinch counter-control). Along with inside position locking and overhook tactics which have proven successful in countless fights, she now has an increased vocabulary of rotational force...which increases the surprisal for opponents. You can see a cut up of this dynamic here: It is a complexifcation of a reduced probability space, introducing an additional axis of dynamic movement, and its attendant vocabulary. There is of course quite a bit of complexity that is involved in the very act of shrinking probabilities spaces into fitness landscapes you've focused on understanding. These can involve hidden skills that require the control over space. Fighting is often a battle over space, and seeking to impose your probability space upon your opponent's preferred probability space. Getting from one space to another makes up a great deal of the art of fighting itself. But, one's growth as a fighter involves constant exposure to surprisal itself (hence the importance of live sparring & freestyle clinch training), so that your embodied prediction mechanisms will be stimulated to increase depth of knowledge over the fight environment, regardless of probability space in its variety. This ultimately involves increased visual acuity, and a soaked-in attendance to pattern recognition, what we've called "growing eyes". We've discussed it before, but the time we've spent with the legend Karuhat has uncovered the various ways in which he was able to read very large probabilities spaces through the detection of weight transfer, and body position alone. It has seemed to us that Karuhat, as he reads an open spaced opponent is often through a felt calculation of changes of probability that arise from how the opponent is standing, where their weight is distributed, and the shape of their bodily disposition (limb positions, head position, etc). He is able to reduce the complexity of what is probable, shrink "surprise", through a genius-level understanding of the fighting art. It comes off as mind-reading. Exposure to new and different probability spaces, controlled exposure to surprisal is that grows the complexity and knowledge of the fighter. If interested we sketch out a rudiment of Karuhat's spatial reading in this article: The Secrets of Karuhat’s Style – Four Internal Games From Southpaw as discovered in this study.
-
Old school muay thai coaches in Chiang Mai
Kevin von Duuglas-Ittu replied to Dmian's topic in Gym Advice and Experiences
Kru Thailand Pinsinchai is pretty old school. A top fighter in his day, technically strong. Has his own gym in Chiang Mai. -
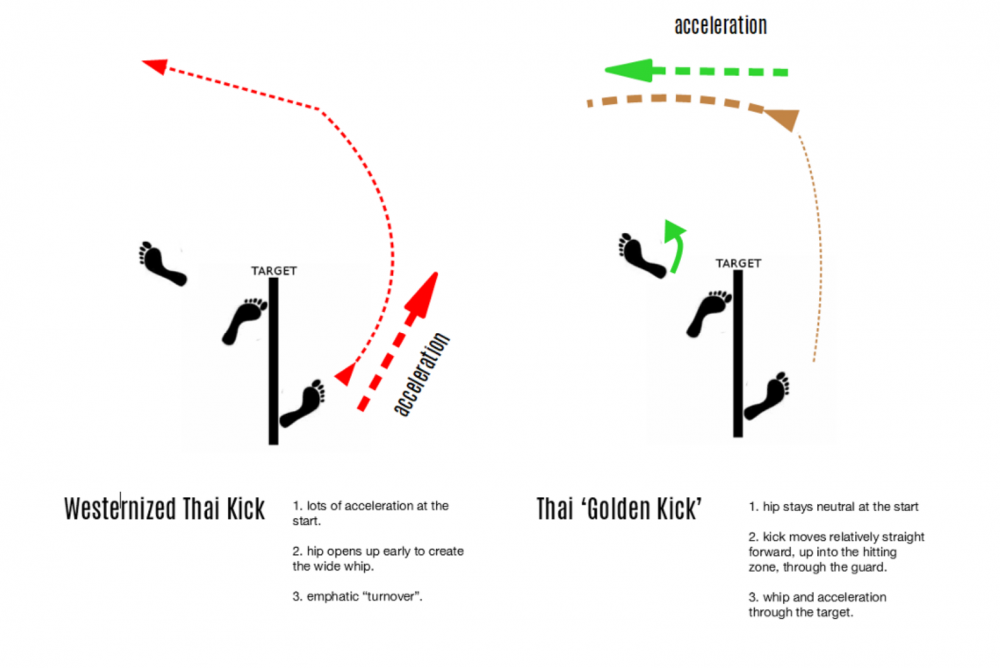
Informal Intro: I've been reading Agamben's The Highest Poverty, an incredibly dry but also quite fruitful study of Early Christian monastic orders used to gain insight into how cultures - and perhaps more importantly sub-cultures - organize and express themselves. He's examining Wittgenstein's prescriptions regarding rule-following and Forms of Life when thinking about Language and problems of philosophy, but tracing these concepts down to their historical exemplification in monasteries in say the 12th century. It's pointedly obscure, but these details open up into flowers of realization, like seeds, especially as I draw them into the sub-culture of Thailand's Muay Thai, and more properly kaimuay (camp) Muay Thai. I've written along this grain on the Forms of Life, using Bourdieu's concept of habitus in Thailand's kaimuay Muay Thai in "Trans-Freedoms Through Authentic Muay Thai Training in Thailand Understood Through Bourdieu's Habitus, Doxa and Hexis", where the hidden, or at least non-obvious, forms of doing something carry secret formative principles which are expressed in the techniques of fighting. But here, below, I want to bring out a very small thought, that aligns with the concept of rule-following and shaped communal ways of doing. Do not pull your strikes. Sorry for the sprawly introduction. Sometimes I feel like I have to really sketch out where I'm coming from because I sense that my frames of reference are potentially quite alien to the topics I'm putting my thoughts to. In any case, do not pull your strikes when sparring. This is why. Strikes Are Like Words Body of Thought: We've probably spoken about this in our lengthy Muay Thai Bones podcasts, but there are many analogies to the Muay Thai of Thailand and language. You seek a certain fluency and ultimately an expression of a grammar and vocabulary that is not your own. There are many points which map in an illuminating way from one to the other, and I think this analogy sheds light onto areas of learning (and performance) that are lost in more mechanistic views of Thailand's strike armory. In some respects this seems ridiculous. "Of course I should pull my strikes, this is sparring! Do you want an all out war!" But, this is the point. A strike in Thailand's Muay Thai is like a word with syllables. It unfolds in time, like a word. And in pronouncing a word which syllable you place the accent on, the stress, is quite important. BE-gone is a mispronunciation of be-GONE. EN-gin-eer is a mispronunciation of en-gi-NEER. When fighters pull strikes very, very commonly what they are doing is radically altering the pronunciation of the strike...they are softening the final syllable. They are pulling it back. This distorts the entire energy dynamic of how a strike is supposed to follow, which involves the communication of mechanical energy through the body parts into the final syllable, which ultimately comes about through a feeling about that strike, in the very same way you would have a feeling about a word, and how it is supposed to be pronounced. What happens is that you feel that in actual fighting you'll just put the emphasis on the final syllable, after habitually placing it much further up the word. Your strikes will have been trained/pronounced with accents often on the FIRST syllable, coming out fast, and then abruptly slowed down and softened. What will happen is that you very well might SAY your strikes louder, even shouting them in fights, but the actual pronunciation of them will be first syllable. You'll be shouting EN-gin-neer!!! Instead of en-gin-NEER. This is because the flow dynamics of how strikes unfold contain a feeling in time, and of emphasis. And sparring is the closest affective training you can have of actual fight circumstances. Sylvie and I have talked about this in the discussion of the Golden Kick: The Golden Kick – How To Improve Your Thai Kick which compares the shape of the Westernized "round" kick, with the more traditional kick of Thailand's Golden Age. Patterns of acceleration become embedded into the very shape of strikes, just as words become pronounced differently: You can take a deeper dive into these patterns of acceleration if you examine Karuhat's particular chest-rising Golden Kick, which is absolutely unique on it is own, but comprises these final-syllable principles to a great degree: #111 The Karuhat Rosetta Stone 7 - The Secrets of the Matador (83 min) watch it here The idea is that in sparring you say your words softly, but when the emphasis on the end...on the final syllable. They come out relaxed and slowly, and have a bite at the end. This actually folds into very high level striking that you'll find in legendary fighters like Karuhat or Namkabuan, who will begin a strike and as it unfold decide if a different strike is in order, mid-strike...because they are looking with their eyes. Elite fighters have matrix-like perceptions of the time unfolding as a strike a delivered, and I think that some of this comes from the feeling that the emphasis, in terms of feeling, but also bio-mechanically, comes at the end. Ultimately you want the affective shape of a strike, and its reality, to express a confluence of body parts all the way up from the ground, through the torso, into the ends of where the strike makes contact. This is a practiced release of energy. The energy does not have to be "hard". It can be quite soft, just as you can whisper a word with emphasis on the end, almost inaudibly. There is something Sylvie's experienced many times when training with legends of the past. Men in their 60s, even 70s. You can feel how hard they are. Some of this is just their "bones", hardened from so much training and fighting as well, but some of it comes through the dynamics of how power flows through their strikes. Sylvie's commented about this for instance with Sagat or General Tunwakom, both in the Library. Even at very slow motion demonstrations of a technique there is a tremendous, or at least unexpected transfer of energy, at the final syllable. It's not that it hurts, it just has a certain kind of weight. This is because they are pronoucing the "word" properly, even in slow motion. The energy is not stalling, or getting suppressed. It's just that very little energy is being sent through the line in the first place. It still has a zing, because these are the shapes of the words. You do not want to lose the shape of words. Especially the old words. If you've been pulling your strikes, and pronouncing them with emphasis on the first syllables it might very hard to change that pronunciation. It could lead to sparring too hard for a while, or unpredictably. Key would be learning to say your words more softly, with lower energy on the first syllable, and learning to feel how they can accelerate at the end. This would collaborate with what you are or can do on the bag or on pads. You want to feel that ascension in sparring, and the control over just how much electricity you are sending down the line. Another Note about the Shapes of Words and Muay Thai in Thailand This comes to a larger concept about the proper techniques one might learn in Thailand. Just because techniques are being communicated in Thai gyms does not necessarily make them purely "Thai", or connected to lineages that are the most effective. This is because the shapes of techniques are like words, and words are effected by the innumerable practices that make up a gym's social space. A kru very well might be teaching the form of a strike as he learned it as a boy and teen in a kaimuay very different than the one he is in at a kru (the social space, the behaviors of fighters and authorities, etc), but the gym itself is a sponge of Forms of Life, and as we, as Westerners (and others) enter these spaces we are also communicating our Forms of Life. How we through punches on the pads can change the way punches are thrown in the gym, how those words are pronounced. How we come OFF the pads and hold our dispositions, how we recover, might very well change the shape of how Thai fighters recover and express themselves. If definitely seen Western-friendly gyms absorb many unscripted but powerful Forms of Life from the non-Thai fighters they train. It becomes a cross-pollination. This is not necessarily even a dilution. There can be benefits of cross-pollination. But insofar as we come to Thailand to find how words - and even sentences, or full paragraphs - are pronounced in their language, in the language of their efficacy, there are many ways in which we can be communicating and impacting against what we are looking for. We come to Thailand and we find what we already are, because others like us have already been carving rivulets into the rock, changing the habitus. This is one of the reasons behind the Muay Thai Library project. We are filming the techniques and affective expression of Forms of Life one cannot really find any longer, because the kaimuay and the promotional muay that produced them largely no longer exist. It's the way words were pronounced, and a great deal of that is a mixture of technical proficiency, the feeling of a transfer of energy, and end of syllable emphasis that holds it own character, a character of a time and place. When Dieselnoi teaches how to knee, he is teaching a feeling of kneeing, as well as a technical unfolding of parts. These feelings are embedded in a realm of Muay Thai that is no-longer. At best what we can do is reach for these feelings, as we scribe the bio-mechanical guidance of what they are.
-
You may find that if you look into the traditional side of Thailand's Muay Thai (how it is scored, and also in many ways fought), there will be some correspondence to the "inner" or "internal" forms of slower martial arts like Yiquan. We've discussed in the Muay Thai Bones podcast where Buddhistic principles such a "Ning" or "Samadi" are drawn on for Thailand's Muay Thai. Here's a link to the whole playlist. Sorry I don't recall which ones, unfortunately they are very long podcasts.
-
I began writing about this here, where the photo series is found: The Inner Grace - The Esoteric of Muay Thai Style This is a continuation. There is an incredible play of doubling in Luce Irigaray and Carolyn Burke's "When Our Lips Speak Together" which slides between the doubling of the Self and Other (a woman an her lover), and the Inner private Self, and our Outward public Self, which is brought together in the analogy of lips touching...and separating to speak a word. That impossible-eqse word is unknown. Perhaps it is "love" or "equals", but it's about the joining of the two. When the separate touch, as one, and then separate out to speak. Some relevant excerpts: And There are some really beautiful things said about exteriority, and also about the internal experience of lips touching lips, the recursivity of the same, the joining together. These passages feel like to me that have taken the abstractions of a Philosophy and pressed them down into experiential physicality, all the while riding on a rich metaphor. I feel like this self-touching of creation is something that the camera can bring to fight photography - well, all photography of course, but the subject here is fight photography. Fights are so externalized, in an apparent sense. Seen as events of clashing. And fight styles signatured by mechanics of force and outward display. The temptation is always to grasp hold of the external and record it as a physicality. But, in photographing Kru Pern, for instance, I uncovered a different layer, one that I described (above) as esoteric. The inner techniques of self-touching and self-relation. I was pretty shocked to see it in the files. I felt something of it compositionally when framing shots, but on crop and edit the internal REAL leapt out. I feel like photography, fight photography in particular, can capture that intimate script, that quiet language, which lays like code and word beneath the outward form, which Irigaray and Burke says is "assuming one model after another, one master after another..."
-
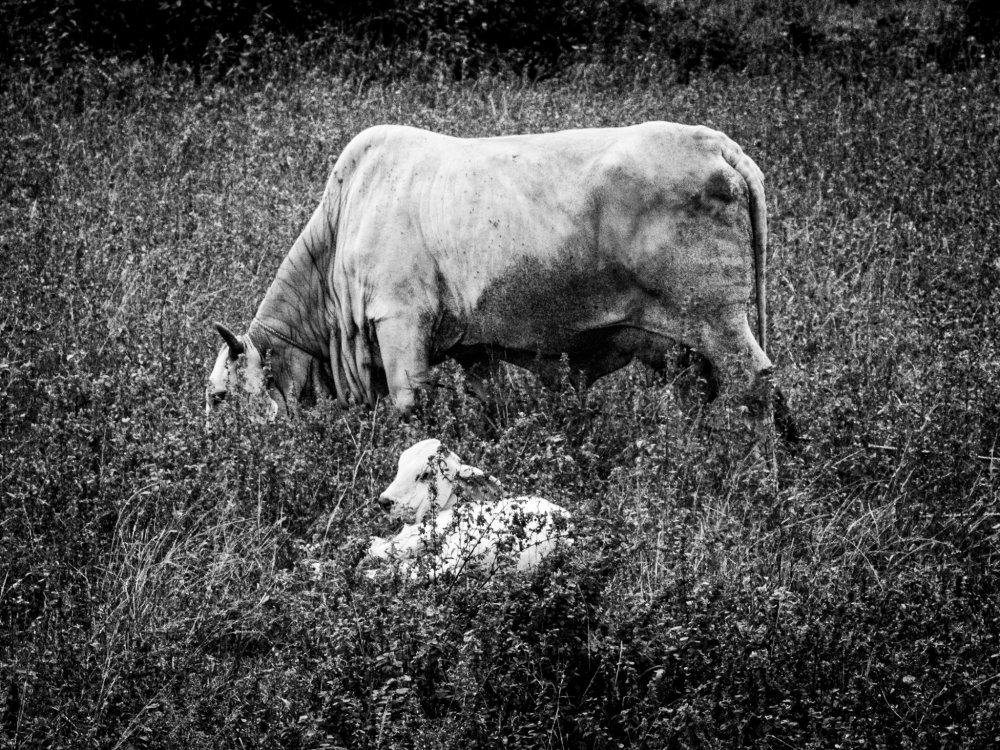
Photography makes a prime example of N-1 rule conditioned inscription, not only how it is framed, but the entire edit of the world, and the edit of the file, not to mention the rote, rule-governed paths of producing photographs. These photographs from today of a calf and a mother are differing N-1 inscriptions.
-
More on N+1 and N-1 from Duchamp and Panes of Immanence TIME AND AGAIN, DUCHAMP INSISTED that the Large Glass (fig. 1) was also (perhaps even in the first place) a consideration on perspective. When Pierre Cabanne asked him how he had arrived at the idea, he replied, “Perspective was very important. The Large Glass is actually a rehabilitation of perspective, which had been completely neglected and decried. With me, perspective became absolutely scientific . . . It was scientific mathematical perspective . . . based on calculations and measurements.”1 To Richard Hamilton he likewise admitted: “The projection [of each part of the Glass] in perspective [on the Glass] is a perfect example of classical perspective, I mean that I imagined the various elements of the bachelor machine first of all as arranged behind the Glass, on the ground, rather than as distributed over a surface in two dimensions.”2 We know that Duchamp drew up several perspective diagrams in this way, to situate the various pieces of his Bachelor Apparatus—now on a reduced scale, now life-size—before they were outlined on the surface of the Glass. from Duchamp and the Classical Perspectivists
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.