Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation since 03/14/2025 in all areas
-
Kevin — this is beautifully written and profoundly resonates with what we are trying to protect. At our gym in Pai, Thailand — led by Kru Sittiphong (Eminent Air, Bangkok) — we often find ourselves discussing this exact tension. The split you describe between aggression as war and tradition as festival maps directly onto the current shift happening in Muay Thai today, especially in the growing clash between Muay Farang and traditional Muay Femur. So many Westerners arrive here asking for two sessions a day, intense sparring, and "hard training" to burn through their fire. They believe output equals progress — but they miss that in Thai Muay Thai, form comes before fire. As Kru says, “If no one corrects your technique, you're just burning energy and money.” You can train for years and still lack timing, balance, and control if no one slows you down. He calls this rush-to-power style "Muay Farang." Not in judgment — but as a cultural observation. It’s mechanical. It’s linear. It seeks transformation through depletion, rather than refinement. It forgets the smile in the sparring ring. The mutual game. The moment when two fighters laugh and say, “You got me.” That ease is the solarity. That’s the festival. Lerdsilla, Saenchai — we show students how they move not to win but to shine. Their movement is gift, not dominance. We see this in our students too — that knife’s edge between aggression and release. Some say they want to spar to “let out the fire.” But this isn’t the Thai way. Not really. Not the artful way. Real Thai Muay Thai is not made in war. It’s made in play, in rhythm, in control, in beauty. Muay Thai was born out of community, not conquest. The rings were surrounded by farmers, not fighters. And even now, the countryside promotions like Pai Fight Night are pushing back against the gambling, the scoring controversies, the drift toward aggressive spectacle. They are preserving Muay Thai as cultural heritage — as festival, as you so eloquently say. Even the structure of Thai training reflects this longevity: one thoughtful session a day, not burnout. Recovery built in. Years spent mastering balance before layering in power. It's a slow art. A patient art. It cannot be "hacked." And it cannot be copied in systems that don't understand its roots. So yes — we’re witnessing a shift. And some, like Samart Payakaroon, are trying to protect the tradition. Others, like the Muay Femur stylist who left ONE Championship, are quietly walking away from the pressure to perform brutality over brilliance. We believe this conversation matters deeply — and must continue. Thank you for holding space for it, — Jennifer & Kru Sittiphong Sittiphong Muay Thai - Technical Muay Femur Training Pai, Thailand2 points
-
I am 5’8 155 lbs. pk Saenchai seemed like a gym I would go to after years of training which I have not had. By the time I go to Thailand I will have 6 months of solid training. (About 13 hours a week soon to be 18.) I am visiting Thailand first, and then planning on finding where I want to make my home base after about 6 months. I have little experience in the clinch, but I know that I want to be a heavy clinch and elbow fighter, as watching yodkhunpon inspired me. I have never seen a fighter that made me want to copy them before. Thank you for the reply and all you guys do.2 points
-
What many do not realize is that ONE has so thoroughly commandeered the social media ecosystem of Muay Thai in Thailand (quite consciously, as part of its marketing approach, absorbing trad social media accounts, controlling messaging across all platforms through various systematically means...and quite brilliantly I would say), that many, many New Gen Muay Thai fans in Thailand, who speak no English at all, now have bought 100% into the ONE Entertainment full power smash aesthetic. Demographically much of it is somewhat a new fan base for Muay Thai, but its very vocal in SoMe post comments, and has influenced the older online gen as well. What we in the West are drawn to in traditional Muay Thai is now is ardently being pushed against by a segment of Thai fandom now, even in the trad ruleset. There is a kind of tug-of-war now between the traditional values of superior fighting and the new International smash values, and hybrid promotions like RWS are kind of caught right in the middle, but seemingly for now siding with trad values for the most part. It does mean though that some trad fighters are just going to go in there and smash on trad cards, which is kind of amazing because this change has occurred in only a few short years.2 points
-
A Battle of Affects I've argued that the highly Westernized (Globalized) affect expression in ONE and other Entertainment Muay Thai, typified in the Scream face you'll see in fight posters (which sometimes ironically looks like a yawn) and in post fight celebration, expressing aggro values that work against the traditional affects of Thailand's trad Muay Thai, a fighting art that comes out of Buddhistic culture largely organized around self-control...(that's a mouthful!) is attempting to invert Muay Thai's relationship to violence itself. It is interesting that spreading in the trad circuit is this mindfulness/meditative post-fight victory pose, an example of which is here, the young fighter with his trainer. This is no small thing because arguably culture is made up of prescriptions of "how you should feel", largely expressed in idealized body language and facial expression. When you change that prescription, in fact inverting, you are challenging the main messages of culture itself. One of the gifts of Thailand's traditional Muay Thai, I have discussed, is that it provides a different affectual understanding of violence itself, which then cashes out in simply more effective fighting in the ring. Something of a gift to a world that is more and more oriented toward rage and outrage.2 points
-
above, festival fight in Pattaya Just some thoughts and observations on the overall state of Thailand's Muay Thai. Not an expert opinion, just an informed perspective. The title of this piece may sound absurd, or maybe for some just an exaggeration, but there is among some long time fans who have watched a lot of Muay Thai in Thailand the sense that the only Muay Thai worth watching in Thailand now, in terms of actual skill, is Muay Dek, the Muay Thai of Thai youth. This piece about why that may be so. There is a sense that Muay Thai has been stretched now in two directions. You have Bangkok stadia, gambling driven traditional Muay Thai, supposedly the acme of the country's traditional talent, and you have Entertainment Muay Thai (with various versions of itself), a Muay Thai that is bent towards - and in many cases just FOR - the foreigner. If I was to really generalize between the two, one line of Muay Thai heads toward more "technical" point fighting and fight management (trad stadium Muay Thai), fights where fighters and corners are always responding to shifting gambling odds, and on the other hand a Muay Thai (in the extreme case of ONE) which is all about combos, aggression and offensive risk taking, emphasizing trades in the pocket and knockouts. The problem is, neither trajectory is very skilled (at least in the historical sense of Thailand's greatly skilled fighters). Muay Thai has become increasingly deskilled, along these two trending branches. And, if you mostly watch one of the two, you might not have noticed the deskilled aspects, because this is just the "new normal", and competition always produces winners who seem in comparison to others, quite skilled. It's only when you take the wider view, not only of the history and greatness of the sport, but also of the present state of Muay Thai itself, importantly including Muay Dek, do you see the drop in skill in adult fighting...as each promotional style squeezes out certain qualities from their fighters, cutting off their full, expressive development. Even with big sidebets on fights (gambling), and seemingly lots of pressure, Muay Dek fighters fight with great freedom. Some of this is a mystery why this is lost, but what follows is a sketch of how Muay Dek fighters change and become limited once they reach a certain age. Why Are the Muay Dek Fighters the Best Muay Thai Fighters in Thailand? If you just watch a few fights, and you have an eye for it, you'll see it. In a word, freedom. In another word, expressiveness. And still an third, sanae (charm, charisma, a key component in Thai traditional scoring). The Muay Thai of the Golden Age (1980s-1997) was filled with highly skilled, very well-rounded, but importantly very expressive fighters, fighters who fought with experimentation who were constantly adjusting to their opponent, drawing on styles and tactics that could in shifts change the outcomes of fights. And in fighting in that way that exuded personality, uniqueness and charm...aura. Much of this quality, and flexibility is gone from Thailand's Muay Thai, but in today's Muay Dek some of it is really still there. Its only when these fighters get to a certain age...maybe 15-16, that it starts to become squeezed out. In the Muay Dek even of today you get fighters who are regulating their energies with great subtitle, not swinging between overt passivity or over-aggression, fighters engage more continuously in the classic style, with fewer ref breaks, less stalling, fighters drawing out extended phrasing and highly technical defensive stretches that endure. A greater variety of weapons, and even transitions between fighting styles or a shifting of tactics, to solve what is happening in the fight, a kind of cerebral aesthetic that older fighters seem to have lost the capacity for. At the highest levels of Muay Dek youth fighting you see dimensionality...and personality. There is much less nibbling at leads. Instead one sees that leads are vied for more or less continually, and expanded when achieved, without devolving into hyper-aggressive mashing. I'm going to leave Entertainment Muay Thai to the side for now, especially ONE which is its own particular excessive exaggeration, mostly because its kind of obvious how promotional hype, booking dynamics, rule-sets and bonuses shape fighters to fight in a certain more limited way. What many may not realize is that trad Muay Thai in the stadia also forces fighters to fight in a certain way, in many cases simplifying or pairing down what they had been capable of when developing as youths. I'm going to say "gambling" here, but gambling is not the boogieman monster that a lot of online commentary makes it out to be. Gambling in Muay Thai is essential to its form, in fact I don't think Thailand's Muay Thai would have reached the complexity of its art without ubiquitous gambling, all the way down to the 1,000s and 1,000s of villages and provincial fight cards, its ecosystem of fighting, which have gone on for maybe centuries. Some of the discussion of the importance of gambling I discuss speculatively here: above, festival fight in Buriram The problem isn't "gambling" per se, but rather that in the larger venues in Bangkok because of the changing (eroding) demographics of Muay Thai the shift of economic power to big gyms, and the dwindling talent pool, the powerful forces of gambling interests have lost proportion, and now have outsized impact. There are not enough counter-balancing forces to keep gambling's historically important role in Muay Thai's creativity, in check. These have worn away, leaving gambling as too prominent. But, I'm not talking about corruption here (which everyone loves to turn to with an infinite finger of blame). I'm actually talking about the way in which Muay Thai is traditionally fought with fighters responding in a live sense to the shifting odds of the audience. Online gambling has complicated this more human, social dimension of the sport, abstracting it to 1,000s or 10,000s of people of varying interests and even knowledge, on their mobile phones. The demographic of "who" gambles has changed, and increasingly people are gambling who have less knowledge about the sport. They'll place a bet on Muay Thai just as they'll place a bet on a football game. Again, let's bracket, let's put the online nature of gambling to the side, and just talk about the traditional relationship between live fighting and live in-person gambling in the stadia. The fighters are fighting TO the odds. The odds are the "score" of the fight, just like in basketball you could look up to a scoreboard and see the score of the game, in Muay Thai you can look to the odds and (roughly!) know the score of the fight. There may be distortion in the odds, whales and their factions of one sort of another may be putting their thumb on the scale, but there is a symbiotic discourse happening between live gambling and the fighters (and their corners). Some of this traditionally has produced great complexity of skills, the ability of fighters to not just "win" the fight in terms of points, but also manage the fight, in stretches, shaping narratives. But today, the exact opposite is happening. Gambling is deskilling traditional Muay Thai, in large part because the small gyms of Thailand - the gyms that actually grow all the fighters, feeding the talent of Bangkok - have been eroding. Not only have they been disappearing (there are far, far fewer of them), those that exist still have no political power in the socio-economics of the sport. When fighters of small gyms enter the gambling rings of Bangkok, not only are they doing so on a very fragile line of income, often losing money to even bring their fighters down, they can no longer bet big on their fighters to supplement fight pay. Betting on your own fighter was once an entire secondary economy which grew small gyms and encouraged them to create superior talents. If you had a top fighter he could be a big earner not only for the gym, but also all the padmen krus in it, aside from fight pay. Because small gyms have lost power overall, political power, they have to live at the margins, which means their fighters have to fight extremely conservatively so as to not be blamed if their fighter loses. They need the backing of the social circles of gamblers. If you lost, it can't be because you took a risk. And because big gyms are going to win (force through political weight) close fights, small gyms have to practically walk on egg-shells in the way that their fighters fight. Generally: get a small lead...and once you have that lead protect it at all costs. Don't do anything risky to expand the lead. And, because small leads are easily lost, fights often turn into a series of nibblings, with both fighters protecting their tiny leads, back and forth. They aren't trying to win, they are trying not to lose. This form of fighting has transmitted itself to big gyms, is the new traditional form of fighting. Don't risk blame. This aspect of "not my fault", "defend a small lead, take it to the end of the fight if you can (5th round), make it close enough and then blame politics or corruption if you lose" has become a normalized style of traditional fighting, across venues among adults. Some of this is because the current state is an out of proportion exaggeration of the truth that traditional Muay Thai fighting always has been expressive of political powers and social capital struggle in hierarchies outside of the ring. Fighters ARE part of and in the ring express social networks. This is part of Muay Thai's social dimension and cultural anchoring. It's just that with the erosion of the powers of small gyms, the dilution of the talent pool, the hoarding of limited talent, has pushed this aspect too hard, and distorted the sport, draining it of skills and its renown complexity. To give a small anecdotal example of how this deskilling works, I remember when a smallish gym was training a fighter, and in padwork the fighter switched to southpaw, just experimentally. No! The answer came back from the kru, and they related a story from the past when one of the gym's fighters had switched to southpaw in a fight and lost. The gamblers who bet on him were furious. He had "blown" the fight. The gym had lost face. From this single event, probably a fight not of much consequence, the gym now forbade switching. It could cost you a fight. An entire branch of Muay Thai (that of switching) was cut off from that gym's fighters...forever. Not only in terms of that technical branch of development, the whole spirit of experimentation and creativity was closed off. The goal was: get a lead...keep it. Don't develop a style that is complex, or varied. Don't do anything in a fight that IF you lose, the gamblers who backed you will blame you and the gym for. This is deskilling. one reason why Thai fighters have been the best in the world isn't just that they have trained and fought young. It's also that they have been at the apron of fights, watched the shape of the traditional aesthetic, socially absorbing a great deal of fight knowledge. At the rope, even as cornermen or impromtu coaches. Its not just the doing, its the participation in the Form of Life that is traditional Muay Thai, bringing a depth of IQ. As small gyms and kaimuay across the country lose power in Bangkok, social power, they have to exist in very narrow economic margins, which means that technique wise their fighters have to fight in very narrow lanes. The spontaneous and the creative is too risky, because gyms don't want to be blamed. Fighters cannot explore or develop new ways of winning fights. There is a secondary dimension in this, as the downfall of the Thai kaimuay is told, which is IF a small gym does produce a particularly strong talent, this talent will not become a resource for the gym, adding honors to the gym (championship belts, etc), growing the gym through his presence. Instead, if you produce a talent this talent will be ostensibly stolen from you. Not outright stolen, but you will be pressured to "sell" their contract to a big Bangkok gym. This pressure will usually come from the fighter's parents, who want success and fame for their son, and the esteem of a bigger name, and it will come from within the hierarchies of the sport. The sale will happen. Instead of a developed talent adding to the richness of a gym's culture and growing their talent own pool of younger fighters who want to share in the glow of gym success, instead you'll be financially compensated with a contract sale. Some money in the pocket, to the gym owner, but not the kind of verdant growth a talent would have brought in the past, something that would shine across all the krus and padmen, and younger fighters in the kaimuay. And, fighters now are being extracted from small gyms younger and younger. The comparison is fruit being picked from trees more and more less ripe. Not only are fighters in general entering the Bangkok stadia with far less experience and development in the past, fighters are also being swept up by big gyms at a much higher rate, at an earlier state of their development. The ecosystem of the small gym, 100,000s of them, is being starved out. And its that ecosystem that historically had produced so much of the foundational complexity that gave Bangkok fighting so much of its renown diversity. Fighters that entered Bangkok stadia used to be much more complex and experienced, and then once they got there the complexity and experience of that scene increased and amplified them, spurred them to greater growth. Now, its the opposite. Arriving in a Bangkok stable may very well nullify your potential. We might add to this that the large big name gym stables of Bangkok today, that have swept up much of Thailand's diminishing promising talent, concentrating it, have become more like holding houses of that talent, and fighter factories for promotions, and less like developmental houses as old Bangkok gyms like Muangsurin, Thanikul, Pinsinchai, Dejrat, Sor Ploenjit had been, promotion favorites which maintained not only a kaimuay developmental creativity, but also more lasting connection with provincial sources. Muay Dek and Facing Power So, the good news is, despite all these forces against creativity, against small gym development, Thailand is still producing very high level Thai fighters from youth. These fighters fight with complexity and freedom, full of sanae, technical excellence, narrative control, quite different than their older counterparts who have learned to strip away their individuality attempting to preserve leads in gambling's stadium Muay Thai. I'm not sure what to account for this other than to believe that Thailand in its heart still maintains the aesthetics and richness that created the acme of the sport in the Golden Age, these qualities haven't been stamped out yet...it is only when fighters get to a certain maturity, when they are fighting for gamblers without a lot of social power themselves, protecting tiny leads, that they lose these qualities. They become deskilled. There is another element to the mystery of why these Muay Dek fighters lose their skills when they age. Kru Gai at Silk tells Sylvie: It's easier to be femeu when everyone is low weight, and nobody has power. Muay Dek fighters develop all this complexity because there is no "power" consequence for their experimentation at low weights. And one can see how this makes a serious amount of intuitional sense. Gamblers today favor more "power" in Muay Thai, so femeu fighters enter contexts where suddenly there are consequences that limit what you can do. But, if you take a moment to think about it, femeu fighting youth of the Golden Age also once they hit a certain age encountered "power" in opponents. But, instead of losing their skill sets at maturity, they actually grew as fighters, became more complex, more creative, more effective...against power. Someone like Karuhat was fighting up two weight classes in the 1990s, a very femeu fighter, against very powerful opponents. It's can't be that encountering the maturation of "power" is the thing that is shutting down the development of the youth, who have already developed so much prior. In fact, there seems a rough parallel between artful youth fighters of the Golden Age and now. Both of them hit this "wall" at a certain age. But in the Golden Age this accelerated their growth, today it stunts it, and even regresses it. I suspect it has to do with the overall conservative form of stadium gambling Muay Thai, the entire incentive and punishment system that produces a lot of tiny-lead chasing...and this goes back to the dis-empowerment and erosion of the small gyms that feed the sport, developing the fighters. The best fighters in all of Thailand are the Muay Dek fighters. It is the closest thing to a natural lineage with the greatness of the past. But right now...there is no way forward for them. No way for them to allow their expressiveness of character and technique to expand and not be disciplined into submission, dulled. They have to face the trad conservative ecosystem, or have to turn to the hyper-aggression of entertainment promotions, each of which robs them of a vocabulary of control and expression.2 points
-
A lot of these thoughts of several years came together for me in side conversation with Arm of Muay Thai Testament Instagram who is looking to perhaps put together a project around Muay Dek fighters of today. I asked him if he could link some present Muay Dek fighters on the rise. This is what he wrote, posted with permission, posted in a series of replies: Strong Muay Dek Fighters Today 1. I was rewatching one kid this morning, as I do with all the kid fights that gets good reception, and this kid from some gym I've never heard of is so good femue. I think the gym is a new addition to Petchyindee's roster now. His name is Kaona Jor. Nopparat The part about Femue being easier to execute at lower weight is so true. Regarding the examples, I only really know the Petchyindee ones but here goes. In no particular order: 1. I was rewatching one kid this morning, as I do with all the kid fights that gets good reception, and this kid from some gym I've never heard of is so good femue. I think the gym is a new addition to Petchyindee's roster now. His name is Kaona Jor. Nopparat2 points
-
This perspective is related to our manifesto of values and a priority on provincial fighting in Thailand.2 points
-
Many are curious or questioning why I’ve become so focused on fighters of the Golden Age, if it might be some form of nostalgia, or a romance of exoticism for what is not now. Truthfully, it is just that of the draw of a mystery, the abiding sense of: How did they do that?, something that built up in me over many years, a mystery increasing over the now hundreds of hours I’ve spent in the presence of Golden Age fighters - both major and minor. Originally it came from just standing in the ring with them, often filming close at hand, and getting that practically synaptic, embodied sense that this is just so different, the feeling you can only get first hand - especially in comparison. You can see it on video, and it is apparent, but when you feel it its just on another order, an order of true mystery. When something moves through the space in a new or alter way it reverberates in you. How is it that these men, really men from a generation or two, move like this. It’s acute in someone like Karuhat, or Wangchannoi, or Hippy, but it is also present in much lessor names you will never know. It’s in all of them, as if its in the water of their Time. I’ve interviewed and broken down all the possible sources of this. It seems pretty clear that it did not come to them out of some form of instruction. It was not dictated or explicitly shown, explained (so when coaches today do these today they are not touching on that vein). It does not seem sufficient to think that it came from just a very wide talent pool, the sheer number of young fighters that were dispersed throughout the country in the 1980s, as if sheer natural selection pulled those movements and skills out. It did not come from sheerly training hard - some notable greats did not train particularly hard, at least by reputation. It’s not coached, its not trained, its not numerical. A true mystery. Fighters would come from the provinces with a fairly substantial number of fights, but at a skill level which they would say isn’t very strong, and within only a few years be creating symphonies in the ring. Karuhat was 16 when he fought his first fight (with zero training) and by 19 was one of the best fighters who ever lived. Sirimongkol accidentally killed an opponent in the provinces (I would guess a medical issue for the opponent, a common strike) and was pulled down to Bangkok because of this sudden "killer" reputation, but he’d tell you that he was completely unskilled and of little experience. Within a few years he was among the very best of his generation. We asked him: Who trained you, who taught you?, expecting some insight into a lineage of knowledge and he told us “Nobody. I learned from watching others.” This runs so hard against the primary Western assumptions of how Knowledge is kept, recorded and passed, but it is a story we heard over and over. Somehow these men, both famous and not, developed keen, beautiful (very precise) movement and acute combat potency without direct transmission or even significant instructional training. The answer could be located nowhere…in no particular place or function. Sherlock Holmes said of a mystery: Once you eliminate the impossible, whatever remains, no matter how improbable, must be the truth.. All these things that we anticipate make great fighters, these really seem to be the impossible here. They were not the keys, it seems. Instead it appears that it was in the very weave of the culture, and the subcultures of Muay Thai, within the structures of the kaimuay experiences, in the richly embedded knowledges of everyone in the game, in the states of relaxation of the aesthetics of muay itself, in the practices of play, in the weft of festival fighting, the warp of equipmentless training, in endurance, in the quixotic powers of gambling, the Mother’s Milk of Muay Thai itself, which is a very odd but beautiful thing to conclude. It does pose something of a nostalgia, because many of these cultural and circumstantial elements have changed - some radically altered by a certain modernity, some shifted subtly - so there is a dimension of feeling that we want not to lose all of it, that we might still pull some substantial threads forward into our own future, some of that cultural DNA that made some of the greatest fighters ever what they were. It's not a hope to return to those past states, but a respect for what they (mysteriously) created. As we approximate techniques, copy movements, mechanize styles, coach harder and harder, these are all the things that make up a net through which everything slips out. Instead, this mystery, the how did they become so great, so proficient, so perceptive, so smooth, so electric, so knowing, stands before us, something of a challenge to our own age and time.1 point
-
For anyone who follows my writings I do not argue for any sense of a "pure" Muay Thai, or even Siamese fighting art history. Quite different than such I take one of Siam and Thai strengths is just how integrative they have been over centuries of development (while, importantly, preserving its core identity). For instance Western Boxing has had a powerful influence upon the form and development of Muay Thai for well over 100 years, and helped make it perhaps the premiere ring fighting art in the world, but Western Boxing itself was a very deep, complexly developed art which mapped quite well upon traditional Muay Thai in many areas, allowing it to flourish. This is quite different than the de-skilling that is happening in the sport right now, where instead the sport is being turned towards a less-skilled development, for really commercial reasons. The story of whether the influx of attention, branding, not to mention the very important monetary investment that Entertainment Muay Thai has brought will actually help "save" traditional Muay Thai is yet to be written. It very well might, as the sport was reaching some important demographic and cultural dead-ends, and it needed an infusion. But, let's not have it be lost, what itself is being lost, which is the actual very high level of skill Thailand had produced...and how it had developed it. Let's keep our eye on the de-skilling.1 point
-
This is the difficult thing, as Muay Thai shifts to a tourism economy. Things like defense and balance development (along with timing) are very hard to develop in fighters. It takes years, and in Thailand much of it comes out of the kaimuay tradition of fighters raised and fighting since boys. Fights traditionally were scored to favor these things and the training reflected their higher-level maturation. They became embedded in the culture, and the significance of Muay Thai in Thailand, part of its "Form of Life". Teaching them required a rich subculture (which today is highly eroded), and knowledge was passed down in a non-instructive way. As Muay Thai becomes turned towards "action" moments, and incorporates the lessor-skilled non-Thai, defensive and balance roots are increasingly not fed, and will starve. Non-Thais become trainers, not developed in the kaimuay tradition, favoring things they can teach well, especially memorized offensive combos (the new signature of Entertainment sport). The deeper enrichments of balance, control and defense pass away, and notably, as fighters are discouraged from displaying these things offense-first, trade-oriented attacks actually become MORE successful. It becomes a self-feeding system of entertainment.1 point
-
I think people are becoming aware that there is a kind of tourism pipeline that has developed, from commercial gyms to Entertainment Muay Thai, put on for tourists. Tourists working for tourists in tourism "shows", (notably a sport redesigned for tourists to win). There are a lot of things of value in these fights, but people are also becoming aware that they are on a conveyor belt that was made for them. The Muay Thai they came for is far from these experiences. It's very hard to work your way free from this "system" which has become pervasively pointed at the Westerner. Gyms face the problem that people come to them and say: I don't want to fight on these shows, under these rules...because this is actually a tourism system. It's made for you. For you.1 point
-
Was talking to Sylvie about this very interesting historical cycle involving gambling in Siam and then Thailand. To be very cartoonish about it, provincial farmers would sell their crop and put the money in the ground, literally burying it. This would take the money out of the economy. Gambling worked as a counter to this trend, recirculating currency...but, when they would come to the capital to sell their crops in the 1900s this worked too much to the extreme. Chinese mafia and dens of gambling would drain them of their payouts, leaving them and their families enslaved (servitude). So, capital Chinese mafia gambling, which was very pronounced (gambling at one point in the early 20th century accounting for more than a quarter of the government's income through tax farms) developed a strong moral taint, farmers would loose their livelihood and fall into servitude in dramatic, destructive trends. King Vajirivudh ended up outlawing gambling in the 1920s. But, there is a kind of moral-economic tension or spectrum, between the money that stays in the ground (a traditional picture), and money that circulates in the wider, urban economy, with corrosive effects. And even to this day you have this pattern in Muay Thai, with Chinese ancestry Bangkok promoters who have been aligned with mafia and gambling (scene as a moral vice still), and the provincial fighter, who comes to the capital, looking to win big. There is a tension between tradition and custom in the land, and the (International) urban Casino. What is interesting though, the custom of local market gambling also is that which shaped provincial Muay Thai itself, which I detail here: On the history and psychology of gambling, I wrote about this here (there you can find the pdf of Gambling, the State and Society in Siam, c. 1880-1945 by James Alastair Warren which is very, very good):1 point
-
https://www.instagram.com/p/DNJE3xmsiks/ This is how far Entertainment has pervaded. Tapaokaew vs Nuenglanlek. Nuenglanlek losing the fight in the clinch asks Tapaokaew to go toe to toe for the end of the 5th round so fighters can get the bonus. This is basically...let's stop fighting a "real" fight, you know, one fighter out-skilling another, and instead let's "put on a show" for the Entertainment bonus. That RWS itself posts this, selling the action, just is a deeper dive into building a "content" generator sport. This is just the shaping of the sport by commerce and moving to online content and in-person tourism, away from in-person passionate, knowledgeable fandom...which I suspect isn't sustainable as a business model, and certainly won't develop the highest level skills (building the sport long term). It's also an interesting reversal of the supposedly "fake" dance offs in the 5th round, now there is a "show" of action. This likely will become a trend as fighters learn new ways to play the 5th round out. RWS has a tough line to ride, as the nexus space, the limnal space between pure Aggro ONE marketing and gambled traditional stadium Muay Thai. These are nuances and changes in that space.1 point
-
There is an entirely separate dimension of gaze economy in mixed-culture gyms that I'd love to write about, but bookmarking here so to maybe pick it up another day, and that is the way in which visiting Westerners enter training spaces and do not even look so much at Thais in the space, for orientation (despite all that I wrote so far above on this), and really look horizontally at other, longer term farang in spaces. Writing even from our first experiences in Thailand, in mixed-culture gym spaces, visiting Thailand even in the most touristed areas can be a very intense experience of foreign-ness, and entering a Muay Thai gym, even the most commercial of these spaces (which are themselves quite scocially agonistic and competitive) can be an emotional experience without compass. One enters these spaces looking for "how to do it", and immediately one takes social cues from all the other Western traveling fighters. The at-first imitative, and oriented gaze is towards longer term Westerners who "know the ropes", eventually will become emulative, because part of training in Thailand is learning how to be a traveling fighter, involving many things other than simply the training. Everything from where and when to drink water, to where eat, to how to comport oneself, the sum total of "how to go about things" largely learned through imitating longer term traveling fighters. We remember - and this is just a small thing - that Sylvie at Lanna so many years ago (Lanna being one of the more established "authentic" mix-culture gyms in Thailand, with a lengthy history), had to mentally separate herself out from the 40 minute hand-wrapping beginning of training that had grown among Western traveling fighters, to begin every morning's training, where you not only wrap hands, quite slowly, coming back from your run (for those that ran, most did a pretty substantial run), but really just talking, shooting the breeze, or just being a part of that mini-habitus of training preparation, sitting on the bench with others, even if you kept by yourself. This was a sub-culture of "how to begin training" that had developed around longer term fighters, really a small thing, but it was its own reality, its own pace, an important part of the traveling culture of the gym at the time, quite apart from the Thai-led training. It was emulative. Our time at Lanna then, but also at several other gyms, made us quite aware of how gyms actually were in laminate layers of habitus, a Thai and non-Thai side, and that long term fighters, or adventure tourists played a very large part in creating and bearing the Western sub-culture, in part because it was constantly fed by new, fairly disoriented participants. ****** We are left with a mirroring hypermasculinity, between two cultures / sub-cultures. The Westerner engages in a Hard Body hypermasculinity, and probably a (pomo) Colonialist adventurist hypermasculinity, and the Thai Nak Muay is participating in a hypermasculinity which somewhat resides in his (her) past, that out of which the art and sport of Muay Thai has grown (Peter Vail cited above). The Nak Muay is encountering the project of developing and expressing the (somewhat classic, somewhat nostalgic) hypermasculinity of his (her) own culture, but also caught in the globalized commerce, the subjectivity of Internationalization, which brings these two cultures / sub-cultures together. The newly arrived traveling fighter from the West is thrown in between these two performances in really what can be a heady, transformative way, emulating well-grounded Westerners, weaving himself (herself) into that fabric, fashioning that hypermasculine identity and performance, that gaze economy, while that masculinity itself has been in the longer term developed in emulative fashion on the Thai Body, at least in terms of the transformation being attempted, to lean into Thai, classic hypermasculinity. In this several things map between the two hypermasculinities, but really many more do not. All this while, Thai Nak Muay in these spaces are also being swept up toward a new, globalized masculine, following the new gaze economies the body is exposed to, including those digital economies of gaze.1 point
-
I realized something watching Chatchai with Sylvie yesterday, that the order of action is quite important to unlocking Thai style. The foot moves, the weight transfers, and then the strike comes. The mind, the watching eyes, are only there to stop the strike from coming. It is like the archer who just draws the bow and lets it fly. String, arrow, string, arrow. But then the mind could hold the string and deny the shot if the timing isn't right. This is how Thais develop incredible speed in their retreating counting kicks for instance. The mind is only there to hold or delay the release, but the release comes from the feet, from that very moment the feet feel the weight. In this way, one is actually thinking with one's feet because every time your feet move and there is weight transfer the thought, a sort of itch, comes. The mind, decision-making, in this dynamic only acts as a retardant. The difficulty is that many, especially Westerners to the sport, have a different cycle of action. They instead look with their eyes, and use their Mind as trigger man. The Mind begins the propelling action, which then goes to the feet which are not properly ordered (and very often not all the way down to the feet at all, at the shoulder, or thigh, and then starts the strike. It is too late. The thought cannot begin there. Not only is it slow and behind the action, but duress from using the Mind in this way, as the trigger finger, produces tenseness in the body, and squeezes all the channels. The strike cannot come, and then its slowness produces further mental stress. And more, the Mind itself, that is the decisioning, trigger-mind, is not fast enough to follow action and threat. It can be pressured by an opponent and the unexpected. It can be overwhelmed. This Westernized problem of the mind is sort of "hacked" by the combination, which is a memorized pattern of strikes which take the Mind as decisioning trigger out of their execution...but, they are in their relationship to each other "mindless" in that they are committed-to in their series, and they do not come from thinking feet. Combinations of this sort suffer from many of the same weaknesses, because the are triggered by the decisioning Mind. Not only are they late, they are easily overwhelmed, because their cycle is slow, and the feet are often unorganized. Key, instead, is thinking with the feet, and if thoughts arise from the feet they can also operate in combinations, with the mind delaying timing or shifting strike choice. But the thought, the itch, comes from the feet...which is why moving feet, the shifting of weight, even subtly, is essential for the flow of thoughts. This is likely one of the purposes of the Thai rock, the rhythm. This is a basic tindering of thoughts. There is another lay of this, which any soccer/football player knows. If you are thinking with your feet and weight transfer springs forth thoughts, then the timing of foot movement becomes central. Steps or shifts or thoughts. In this way for instance a Thai will time the backstep in a retreat and counter such that the foot falls precisely at the opportune time of interception of an advancing fighter. This means the Mind as decision-maker has almost no role at all. The foot retreats, with dance-like sensitivity, and the strike comes. The fighter is tantalizingly close, but yet too far for the opponent, and the strike is almost unseeable. But the same is the case for weight transfers in the pocket, the art of boxing is made of this. The speed of this is mimicked in "combos", but memorizing combos are not thinking with the feet. They are just trying to cut the Mind out in their succession. Because thinking with the feet is so important, things like constant shadowboxing such that the feet develop the capacity to think, create and improvise, and light, equipmentless sparring, which is like shadboxing, both are central to building the classic Thai style which is marked by ease of movement and its speed of perception. Below, Yodkhunpon on shadowboxing: These are related thoughts on stress and delay producing "Precision" training Precision – A Basic Motivation Mistake in Some Western Training - In that article the decision cycle is talked about in different terms, tracing the rise of tension in the cycle, which is really linked to the decision-making Mind.1 point
-
In this mix of conflicting Bodies of race, class and valorized ideals - literal bodies clashing - is the larger context, aside from what may have been the author's experience, that larger bodied Westerners are pitted against lighter bodied Thais (in the purported scale of fairness), and that since COVID under the imperatives of Soft Power a new ruleset style, "Entertainment" Muay Thai, has pervaded, which is designed for the somewhat explicit purpose for the Westerner to win fights. That is, in the balance of emulation that the author outlines, the way that fights are actually being fought and scored has been skewed against the demands of emulation itself, not without Colonialist overtures, especially in topography of the article. This is to say, changing the rules takes some pressure off of promoters and gyms to arrange "dives" to ensure the positive experience of emulative transformation. Now Muay Thai, larger bodied, can be fought in a more Western style, favoring Western skills. At minimum this further contrasts or perhaps complexifies accounts of danced-off 5th rounds, as signatures of authenticity.1 point
-
In one almost categorical sense, nothing is more Colonialist in sport than changing the rules of another people's sport so that you can win.1 point
-
Recently really feeling the pain of the reality that Muay Thai is washing away. There are just waves and waves of shallow commentary and sharing, content hypes, and mostly just an incredible forgetfulness in our highly digitized culture of imitation and wasting. Do think we have done something with the Muay Thai Library documentation, and are doing something. It's an edifice, a seed bank of knowledge, but I honestly don't even know if what it is will last even 10 years from now, as the sport careers off into the service of the Westerner. Do people not even know that they changed all the rules to let you win???? And that Thailand itself is no longer producing the same highly skilled, deeply founded fighters? Today just bummed by it all. Definitely Benjamin's Angel of History bending down, grasping at windblown scraps. All I can comfort myself is with the fact that Thailand's Muay Thai has been incredibly resistant and resilient to incursion and outside influence, for centuries really. And it will last through this. But, we have Karuhat today sleeping in the extra bedroom, his knee recovering from ACL reconstruction, maybe with ten years of free movement left in the joint, and my heart is breaking because he is the GOAT in his own way, and people just aren't going to know him. And there are layers and layers of such memory, and capacity.1 point
-
As Thailand's Muay Thai travels toward pure commerce and its consumption, it should be remembered that the Thai fight for the dead, before the dead...to the honor of the dead. In funeral rites for fallen fighters and figures of the sport it is customary, in these days, to perform a traditional fighting wai kru and to put on a theatrical display, a show fight (though even further back, and at times, it can be a real fight a reality marked often marked by wagers taken). There is a celebration of the art, the sport and mostly of the community of people within it, all present in the memory of the past nakmuay or figure of the sport, who is no longer with us, and certainly a kind of joy when it comes to the spectacle of the sparing fight itself. When people argue that Muay Thai is just a sport, they do not realize that Thais in the sport have the custom of putting on show fights for the dead who have left. It is far, far more than a sport. It is the weaving of meaningful violence, transformed into spirit and its dignified glory. Each and every fight, and each and every ceremonial spar and wai kru. Below three videos of ceremonial fights. The second one is part of a longer short film on the passing of the legend Sirimongkol. Dieselnoi and Pudpadnoi for Namkabuan Sagat and Pudpadnoi for Sirimongkol Yodkhunpon and Chatkating for the head of the Sittraipom Gym's passing Samart and Weerapol (not sure which passing)1 point
-
Never sure about provenance, but below is a photograph marked as a Funeral Fight for Marupongsiripat (1898). This custom reaches back well over 100 years, and to Thai royalty. The establishment of the 3 Schools of Muay Boran (just before the decade when Muay Thai would be modernized on the model of British Boxing) also occurred through funeral matches.1 point
-
I'm not sure which entry or post you are responding to, but I'm glad to hear there is resonance between the things you believe and the things I write about. This is going to be a struggle, but as Muay Thai turns harder and harder towards Western values, altering its training and how fights are fought, scored, etc, in an attempt to drive tourism numbers, I believe the lasting and passionate Western tourist will end up yearning for a Muay Thai that is not made in their image. They didn't come 8,000 miles to see and know what they already know and feel. I believe Thailand's Muay Thai has something very important to teach the West, especially on the nature of violence, as it is addressed in the sport (and art). I believe things will bend back...but not before a lot of damage is done, and not before many things will be lost. We just have to do the best we can.1 point
-
It was just a perfect storm of a very deep talent pool, in the provinces, a huge economic boom in Bangkok with lots of money to invest, and the provincial (boxing educated) workers flowing into the city. The influx of workers was likely a significant factor. It created a hungry, educated and impassioned fan base. writing about Dieselnoi and Samart The so-called Golden Age of Muay Thai in the late 1980s and 1990s was driven by the economic boom of those years. Not only was there heaps of money to invest in gyms and fighters, flowing to enlarged fighter pay and sidebets, but it was the provincial man, the workers, who swarmed to Bangkok to find employment in the suddenly burgeoning, cosmopolitan economy. It was they that filled the stands with their wages in their hands, betting them. It was they who bought the newspapers and magazines. You have to add in things like the particular brilliance of the promoter OneSongChai who was expert at staging drama, pitting particular styles against other styles, and nurturing the talent of fighters without owning a gym himself. Another hidden factor could be that the influence of Western Boxing on Thailand may have also been its peak (there were boxing fights on each and every card, both at Rajadamern and Lumpinee, 9 cards a week - that's almost 500 boxing fights a year at the National Stadia). The mix with Western boxing may have even further expanded the fight skills of the talent pool. Amateur boxing was a very big deal in Thailand, especially after the King built provincial stadia across Thailand in 1979. These hubs of stadia likely anchored provincial fighting. Also, just structurally, the Muay Thai of then was not dominated by only a handful of gyms that simply bought talent up, as it is today. There was greater variety of BKK gyms, drawing from many more gyms in the ecosystem of the provinces. Even to get to Bangkok, it is said, required a great number of fights and proven skill. There was also great regional pride, and identity in the growth of fighters. Karuhat told us that every fight he had in Bangkok, when he was good, would pull 4 bus loads of fans from Khon Kaen in Isaan (his home town). This deep regionalism just doesn't exist in the same way now. The 1980s/1990s was a period of growing National connectivity, in the context of still powerful regional identities, expressed through the fight scene. The above is from a Reddit comment I made a few years ago. It seemed best to anchor it in my sub forum somewhere so as to not get lost as its a pretty decent, short summation. A few things that changed TLTR The economic boom in Thailand ended in 1995. In the 2000s there was also a rule change allowing sweeps and trips that were illegal in the Golden Age. This ended up radically altering the clinch fighting & grappling that arguably fueled much of the the complexity of Golden Age fighting styles. Boxing gradually started losing its influence on Muay Thai, until today there is next to none. Along with socio-economic, demographic shifts (changing the talent pool and the fan base) pedagogy & training methods seem to have also gradually changed as well, eventually accelerating the decline.1 point
-
If I was answering this question today I think I'd expand the picture of Western Boxing's lasting influence, coming up through the decades, intensifying from the 1960s on, the Army and Police Boxing leagues and I'd also write about how television was just starting to Nationalize Thai consciousness, and the built out local television networks in the Provinces, local stadium hubs, the published rankings from the provinces and the wide-scale small kaimuay ecosystem (which has been almost completely eroded) which developed so many fighters for the stadia. Here you can see how deep the provincial rankings went in published Golden Age Muay Thai magazines, layers of talent outside of the Capital (originally posted to Reddit Here are some Golden Age related Muay Thai economics, as well:1 point
-
The TAT in Thailand put forth its huge marketing strategy for tourism investment, detailing a budget of about $140,000,000 USD, but notably Muay Thai is almost entirely absent of mention (other than the large scale Wai Kru Ceremony which I believe is aligned with the Amazing Muay Thai campaign. read it here: https://www.tatnews.org/2025/07/thailand-launches-the-new-thailand-vision-to-redefine-tourism-in-2026/ Most notably is ONE's absence, especially in the list of the kinds of international sport events that its trying to be included in, "...marquee events such as the Amazing Thailand Marathon 2025, the 33rd SEA Games, and Honda LPGA Thailand will reinforce Thailand’s status as a premier sport tourism hub" A lot of ONE's argument has been how it is radically separated itself out from Thailand's Muay Thai, as part of a larger internationalist sport and martial art entity, in a way that traditional stadium Muay Thai is not. Instead it seems that the overall strategy of the TAT - which I was pretty impressed with, especially went it got down into the segmentations in the lower half of the article - has turned against the very exaggerative metrics that ONE likes to generate and turn to. It wants more meaningful tourism experiences, culturally and locally defined, anchors of attachment, not pushing big numbers which can vacillate and change at the drop of a hat or an investment rate. This is one of the problems with chasing the algorithm and turning traditional Muay Thai into a digital content (knockout) machine. You just become another piece of entertainment whose attention can slosh towards you or radically away from you. The TAT seems to see these and has turned against just number chasing. The kinds of values being put forth actually seem to mirror some of traditional Muay Thai's greatest strengths, the way it is culturally bound, locally defined and experienced, sewing itself into the very fabric and geography of the country. While Rajadamnern's efforts at Entertainment transformation also are not included, it and traditional Muay Thai in general, seems much better positioned to enter into the kinds of expenditures and themes the TAT is taking on. Thailand wants meaningful experiences, cultural attachment and identity, uniqueness, impassioned connection (not social media arguments and memes), it wants travelers who will return and return, who will spend lengthy time, this is traditional Muay Thai, and the Muay Thai of Kaimuay Culture.1 point
-
Note to self...want to write of the female fighter as axis mundi, the christological (in Simone Weil sense of bridging sacrifice) pinning of the body down the in the turpitude of struggle, eliciting the sparks of the divine. Soliciting the female as artist, who builds the ladder to Heaven of oneself. see Possession (1981). What do I mean by this? Some of it is in relationship to my overall theory of ring fighting in Thailand as a rite, and I think my short film was tapping into this intuition:1 point
-
In thinking about Muay Thai training techniques, and the deploy of techniques in fighting, I always turn to a chess analogy. There are "bad" moves one can make against mediocre players, that are in fact "good" moves in terms of results. But, it feels questionable to learn and train "bad" moves of this kind, not only because you might run into a strong player - you might, or you might not - but also because when you learn bad moves, and don't see "why" they are bad or weak, you just don't understand the game at a necessary level. The whole point of looking at moves and thinking about this is understanding the underlying principles that make moves (or tactics, or strategies) good or bad, so that in thinking at that level, you can creatively and spontaneously create novel moves for a given situation. There is an interesting sub-example of this floating out there, the "don't turn your lead foot on a hook in Muay Thai because you'll get kicked". There are layers to this idea. The first is the idea that "sure, you can get away with this against a poor opponent, but if you fight a good one, you'll get kicked". Sounds good, sound penetrating, along the lines which are above. But, not the case. There are any number of ways that this isn't really a readymade practical danger, no matter the skill quality of an opponent. Strikes always exposed oneself to counters. The efficacy or dangers of strikes relies very heavily on set up and situation. What is your range? What comes before and after? A 100 questions that matter. There isn't really just a "if you do x, y will happen", and a lot of the discussion of techniques falls into this error. You can't boxing slip or you'll get kneed. You can't body punch or you'll get elbowed. There are always trade-offs, and its important to see potential weaknesses, but honestly getting calf kicked with a turned foot (which isn't likely to happen at the right distance in most effective hook throwing scenarios) isn't that much different than getting your calf kicked without your foot being turned, in fact if you are weight transferring to your back foot its probably not a major problem...and if its a problem, you adjust. Is your foot outside the stance of your opponent? How far are you, what is the distance? Are you proximate enough? What did you just throw? What are the trade-offs? Inotherwords you need to look at all the pieces on the board. Instead you just get meme'd wisdom. If you do x, y will happen. This is the layering of the chess analogy. This is when we think about the larger picture, the larger principles. In some cases turning your foot may not be optimal, but in others it may give you several trade-off advantages. Some of this goes to the philosophy of the hook itself, why you are using it and how are you generating power? In general though, its worthy to move past the "it works it must be good!" assumption, because there may be larger principle reasons why it will not work against a better opponent, or, the success of the technique may mislead you into thinking a whole class of approaches are fundamentally sound. But, on another level, any question of soundness because of reason "x" also has to be put in larger context of how it matters how a strike is executed, how strikes work in concert, and the trade-offs of offense and defense.1 point
-
Geez. I spent the whole night watching all 11 of the existing fights of Wichannoi Pontawee, who many legends named as the GOAT. I've watched his fights before and have enjoyed them, and a few times wowed, but I felt like he's just too important a fighter to be only "somewhat" familiar with him. I had crisp idea of how he fought, and I saw him have some spectacular moments. But its an entire different thing to sit down and watch all the fights - taking lots of notes - back to back, one after another. I don't think I've learned as much watching any other fighter. It's remarkable. Hopefully I can put these notes together for others.1 point
-
One of the great ethical difficulties to the above is: Do you want to make visible what is currently invisible to the cartographic appropriations of colonial capital? Or, just let them sit safely out of range, in their unseen character? On one hand it feels like you must make them visible so to marshall forces to protect and safeguard, and even possibly restore; on the other hand by mapping the invisible then you just set the conditions for appropriation and distortion, and eventual elimination. One of the aspects which I believe kept Thailand's Muay Thai so resilient, despite so many international influences (probably for 500 years even), is a certain kind of hermetic quality to provincial Siam/Thailand, the way that there are cultural dividing lines, which provincial ways of life and culture exist in their own right, than you are passing into another "land".1 point
-
Watched this fight yesterday, and was really moved by Devy. Looking back at Bill's skills he's everything Entertainment Muay Thai dreams of for a fighter, mixing combinations with Thai techniques, eyes and timing. Beautiful stuff. But Devy is incredible...in such a subtle way. He's like: I'm take your pyrotechniques and just hold position and cover, then move the set, take, hold blast a lowkick to your back thigh. It's like watching a chef cook a masterpiece with 3 ingredients. It really doesn't matter who won this fight, its up over 150 lbs, its the art of this cloistered, minimalist fighting, and his shrug-offs of the aggression and attempts to intimidate. Bill probably the most skilled Western fighter in history, but something deeper and older going on here with Devy. Something that is almost painful to receive beamed across the decades to here and now, as everyone is trying to push Muay Thai into Entertainment and Westernization, Globalization.1 point
-
Saenchai with another KO win on Entertainment Thai Fight. He's the last magical fighter of Thailand, that last of Thailand's greatness, and we are all blessed as he continues in the ring. I don't watch it much (or any of Thai Fight), but still consider it a blessing. When he stops it will all be gone, even though this is kind of half-fighting, and surely he'll do show fights after his retirement. What I love about this photo - and the first thing is that it suddenly feels like Saenchai has aged, and this happens - but what I love about this photo is that you can see his "coal eyes", which is what I call them. There was an old trainer at Lanna named Nok, who when you trained with him his eyes, if you got any advantage or edge, would just turn black. You could see, he just went into that state. And you knew, stop fucking around. Saenchai has always had such a joyful, playful visage, and a charm of handsomeness that he carried everywhere, even into intense battles. But every great, experienced fighter, even Saenchai, has "coal eyes" inside of him, they have to or they couldn't do it the way that they have. And, in my poetic view, it feels like in this slightly aged photo you can see his coal eyes come out. And its really beautiful.1 point
-
I thing that many people miss in assessing ONE's future, or even capacity to do anything, is that almost everything you know about ONE (aside from financial declartive documents, and the few voices that escape NDAs and non-disparagement agreements), has been told to you by ONE. So every concept of "reach" or success that is measurable or on a scale comes from the ONE picture building. And...its a bit like asking Trump how his Casinos and buildings are doing. A good, if small, example of this is how RWS is far exceeding ONE Thailand in revenue, by a factor of about 6. source It just shows a very different concept of business. RWS actually wants to generate revenue at the gate, ONE much rather would pack houses with loads of given away tickets and project massive success through its social media agreements and message control. ONE is trying to generate (one might even say "fake") the feeling of a massive moment...because everything is basically a commercial for the next investor round. They much less want actual fans, so much as the vast impression of fans, and spending everything they can to create the impression is a priority...because the "real" revenue" is a massive investment round, unfortunately something that seems to be drying up. They aren't selling the sport to fans, they are selling it to investors. Sizzle, not steak. So any kind of picture we draw from is already part of this enormous Image creation, which it was hoped would bootstrap itself through dramatic gestures of largess. Flaunting huge payment numbers, etc. A form of "Mystery"... Which isn't to say that none of this is good. The world, and especially the "good" of Capitalism, is made from ostentatious pretension. There is in the world the whole "escape velocity" theory, the fake it until you make it, and when fueled by more than half a billion dollars there is a lot one can fake, in fact the faking becomes quite real, affects real lives, turns into power, creating new capacities and opportunities. So, one of the most compelling questions about what comes now is that the actual question of revenue and profit making, peeled away from the presentation of profit-making, gets put up against other forms of Thailand Muay Thai that are pulling revenue. And, because so much of what has come to us has come through the filter of ONE's image making its very hard to know where anything is at all. Everything is bigger, better, about to break through. It's the Golden Rule of Trump-like positive image driving, which when looking at the world does lead to power itself. Invest now! Buy now! You don't want to miss out on this once in a lifetime opportunity! A certain kind of power. We of course should not be lead astray into thinking that Thailand's Muay Thai does not develop and express itself through all kinds of power relations, many of them institutional, many strongly divided by class differences and entrenched hierarchies, There is no "innocent" Muay Thai in the sense of a Muay Thai without efforts of domination and control, in fact the art and sport arguably is the ritualized performance of such. It's more though that maybe this form of economic magical portrayal, as it is so globalized, so hyperstated, so flowing from that which is outside and beyond Thailand, feels like it could be destructive. Too much sizzle...too little steak?1 point
-
The race for cheaper "grassroots" labor to fill Entertainment Muay Thai cards is on. Rajadamnern vs Lumpinee, trad Muay Thai vs Entertainment Muay Thai. This is the next economic challenge for the sport. Who can tap the rural fighter labor source better, as the trad festival fight culture that has feed the sport for over a century is quickly eroding.1 point
-
I have to say the whole "Sport's Science" invasion of Thailand's Muay Thai, including both the real and psuedo-real, as well as outright con manifestations, as it comments on Thailand's Muay Thai, situating it as somehow primitive in its knowledge of itself, less efficient, or non-ideal...just strikes me as a vast colonialization. A lot of this in the Strength and Conditioning market place of internet ideas. Experts of every kind who are detached from the very notion of craft and artisan knowing get not only lost in the abstraction of their principles, but also in the commerce of their identities a lot of the time. And, quite often, they do not even understand the principles or dynamics that actually win Muay Thai fights...they have instead a kind of two fold assumption: The faster, stronger more enduring athlete will just tend to win...and, secondly, the cartoon (and often dead wrong) understanding of the actual physical characteristics that trad Muay Thai draws upon, then shapes that overall imaginary picture of physical superiority. To indicate just how far off this whole approach is - and I don't think this is an exaggeration - probably being strong, fast or enduring, each of which is less important than being relaxed (which actually makes you performatively more of each of these), which is essential to trad scoring and superiority. And, the usual S&C approaches to each of those tend to actually produce the opposite of relaxation.1 point
-
Not to make a religious point, but rather a cultural one, this picture of "Buakieow" Jalili Barnes in victory is also an interesting instance of cross-cultural expression and value ideal. Jalill I believe is a fundamentalist Christian of some kind (sorry to be vague, it's only something I have cursory knowledge of, and I'm not sure how these denominations refer to themselves) and is known for his adherence to a much more "traditional" Muay Thai path as a farang, mostly shunning entertainment Muay Thai promotion and instead testing his metal in the trad stadium circuit. He just fought for, but did not yet attain the Omnoi belt. Muay Thai itself, in Thailand is cross-cultural, or mixed cultural on the religious front as the South features prominent Muslim fighters through out much of Thailand's history, and who have signaled their faith in the ring ceremonially.1 point
-
Here is something else I wrote that could help with understanding the notion of authenticity in Thailand: How Traditional Muay Thai is Taught Much Differently Than in the West There is a bit of Philosophy in this, it may not be everyone's cup of tea. Posting these ideas here if only for diversity in the way Thailand's Muay Thai can be discussed and appreciated. Traditional Muay Thai (as practiced in Thai camps, kaimuay) is probably best understood as developed through a horizontal, communal process rather than top-down instruction. Instead of rigidly copying an ideal form, developing fighters sync with the group — a kind of shared rhythm or “group mimesis”— which allows for individual expression within collective coherence. Everyone’s technique (like a kick) is different but still resonates with the camp's shared feeling or aesthetic, a pulling toward a social gravity like synchronizing metronomes (video linked below). This more organic, culturally embedded process contrasts with many Western pedagogies, where fighters often perform near-identical techniques due to top-down coach correction, emphasizing biomechanical uniformity. In contrast, Thai camps foster diverse, but affectively aligned, and culturally embedded technical expression—a development perhaps more akin to inner-city basketball or favela soccer, where skills develop in peer-based, play-oriented ecosystems. To be sure kaimuay are very hierarchized status environments, something visiting Westerners may not notice, but a peer and play based dynamic is essential. The nature of this more organic quality poses resistance to the exportation of traditional techniques into abstracted, idealized biomechanical forms governed by a correcting authority. (In Philosophy this critique is mirrored by Gilles Deleuze's rejection of Platonism—opposing the notion of a perfect form with imperfect copies.) Instead, trad kaimuay Muay Thai preserves a virtual/actual dynamic where technique emerges from shared affects and a communal environment, not a replication of a form. Karuhat’s unique kick that we filmed in slow motion is a good case study—its essence can’t be reproduced by biomechanical mimicry alone, as it developed through years of communal, affective practice, as well as extensive development in rings. Our video documentation may transmit aspects of it, but its soul lies in communal resonance, not biomechanical approximation. So, the only way into this kick is through feeling. you can click through to the notes on this, which includes some of the video reference. These points were made through ongoing conversations I'm having with a biologist/philosopher who studies biology through Deleuze and Simondon.1 point
-
A little bit more on the gentrification of American Basketball, with the emphasis on drilling and trainers, and not on expressive play-based development. Muay Thai as well is going through a gentrification, both internally and externally.1 point
-
I'm exploring two aspects of (seeming) spontaneous order (complexity) in Thailand's traditional Muay Thai. At the level of fights themselves there seem to have been a market dynamics in betting customs which drove diversity and escalating skill level, and within the traditional kaimuay there seems to have been an individuation process in training which also escalated skill level and diversity (or at least individualized expression), each of these with not a great deal of Top Down structuring, steering. I'm searching for the nexus between these two "self-organzing" dynamics, which may really be more complimentary, social systems.1 point
-
I am going to Bangkok in a few weeks and plan to stay there for one month, working remotely. I'm coming off a 1-year hiatus and will need to slowly ramp up my training again, so looking for a place that I can pop into 2-3x per week to start, and then slowly progress. I am a casual student so don't think training camps are for me right now. I also want something in between traditional and Westernized - just a gym culture that is welcoming to intermediate women, and makes sure that egos are checked at the door (I've been to way too many gyms holding pads for large, powerful dudes with egos that went unchecked, which led to a lot of unnecessary injuries for me - part of why I took a hiatus). Given this, I wonder if taking just private classes is better, until I "sniff out" the vibes of the other students, before holding pads with them.. I've been looking through lists on here and quite frankly, overwhelmed by the choice. Budget-wise, id like to keep the privates down to less than 40/hr Anyone have recommendations?1 point
-
Zooming out my kind of rough-sketch evolutionary dynamics of Siam/Thai Muay Thai, over the last maybe 500 years. One of the factors of Siam/Thailand is that land worked something like "sea". There was a LOT of it (much more than population which was sparse) and it was hard to traverse (other than waterways). This set up Galapagos-like islandings of local market dynamics, around festival fight rings. But, through seasonal population capture and relocation, and then corvee labor cycles, these festival islands were continually churned back toward city (trade) centers, and martial service (structuring)...which in turn was exposed to quite vast international influence/cross-pollination. You had flows of trade from across the civilized world, cosmopolitanism, martial service, and then constant cyclical return to village micro market ring dynamics, a return to Galapagos variability and selection creation.1 point
-
As Thailand's Muay Thai more and more turns its face toward the World and the West increasingly those coming to Thailand to seek out, experience, train in, fight in, even commit to and honor authentic Muay Thai will have a hard time finding it. In this brief article I want to point out the two biggest areas of difficulty. Keep in mind, I'm writing this from the perspective of having witnessed my wife who has fought more times in Thailand than any non-Thai in history, coming up on 300 times, as a fighter who has steered as clear as possible from aspects of the sport which are arranged or made for you, and become perhaps the foremost documentarian of the sport and art. Everything I describe is from often repeated things we've encountered, found ourselves in, worked through, and what we've learned from the experiences of others. Importantly, pretty much everyone who has been in the country a long time has their own experience and understanding of authenticity, and this is just ours. Thai culture, and Muay Thai culture is also a very complex and woven thing, it is not homogeneous or made in one way, so these are benchmark ideas and there are many exceptions. Authenticity, that which is not made for us. 1. Increasingly Thailand's Muay Thai is made FOR you One of the first challenges is honestly that of recognition. Because Thailand is so culturally different, and Thailand gym training not that of than Western and international gyms, whatever you are experiencing is going to feel authentic. Its authenticity will come through in everything that is different. It must be authentic because I'm not used to this. And because we can only judge from our own experiences, and from what we see and read, this is difficult to overcome. After 3 months in the country you are going to feel like you have really penetrated to the heart of something really new. After a year, you really will feel like you know what's going on, and if you have gravitated toward "authenticity" you'll probably feel like you are in a pretty "real" place. My caution is: Nope. You probably don't realize how much of Muay Thai has been turned toward YOU. And if it wasn't turned towards you, you wouldn't be participating in it. This is going to sound harsh, but pretty much ALL Western/International Muay Thai experiences are something like an elephant ride. The elephant (Muay Thai) is very real, and there is great privilege and beauty in being on an elephant. You're touching a living, breathing, REAL elephant...but you are on an elephant ride, made FOR you. Now, there are all sorts of elephant rides. There is the one where they walk in a circle and you get off, and another where you bathe and then bareback like a "real mahout" would, and then maybe all the way up to 10 day safaris, trekking on elephant back (is there such a thing?). But it's still an elephant ride. You get in the ring, its real...even if its arranged for you, its intense and real. You hit the bag, you burn the kilometers in road work, its real. This isn't to say anything is inauthentic. All of Muay Thai in Thailand will change you. This is about reaching, as passionate people will, those aspects of the sport and art that are unique to Thailand itself, that may fall from view as Thailand turns its face toward you. The Rules, For You How do I mean this? The rules of the sport have been changed so that you (in a less skilled way) will win fights, or perform well in fights you might not otherwise in the traditional Thai version of the sport (there is a full spectrum of this, stretching from RWS entertainment Muay Thai to ONE smash and clash). This is a fairly recent transformation, covering perhaps the last 10 years. The sport itself has been altered for you...and, as it has been altered for you, this also has washed back onto trad Bangkok stadium Muay Thai, which has absorbed many of the entertainment qualities which are pervading social media and gambling sites. In some sense the "authentic" traditional Muay Thai of Thailand doesn't really exist in promotional fight form anywhere in the halo that tourist and adventure tourist has reached. It's just a question of degree. The issues and influences behind this in trad stadium Muay Thai are more complex than this, but it too has turned its face towards "the foreigner". Some of this is just what people like to call "progress" or "the force of the market place" or others might call the "deskilling of Capitalism", but just know that in the fights themselves, they are by degrees turned towards YOU. It really might only be in the festival fight circuits of the provinces where you will still will find the culture and aesthetics of the sport and art FOR Thais. To be sure in festival fights there can be matchups that favor a larger foreign student of a local gym, which has relationship ties with the local promoter, especially if there is no sidebet. But the EVENT isn't for you, designed around you, catering to you or people like you. You're the oddity, and the rulesets and aesthetics have been less altered if at all. The Training, For You On a deeper level, the training in gyms is also made FOR you. The traditional pedagogy of Muay Thai, the manner in which it was developed through youthful circuit sidebet fighting, the kaimuay culture of non-correction and group dynamic sharing of a grown aesthetic, has been seriously eroded, supplemented and sometimes just outright replaced. You are (likely) not learning in the manner of the Thais that produced such acute excellence so many decades ago. Yes, there will be obvious things like farang krus and padmen in some gyms (many of them quite devoted to Muay Thai, but not produced by the subculture), something that is increasing in the sport, but, subtly, even if your padman is Thai, he may not even be an experienced ex-fighter, as mid-so Thais are holding pads now in the growing commercialization. Muay Thai is experiencing a gentrification and an internationalization at the gym level. Beyond padmen, the very manner of instruction and fighter development will have been changed in some sense for you. For one, increasingly you'll notice "combo" training, memorized strike patterns, which is both a deskilling of the sport (making it easier to teach, replicate and export), but also is training that is geared towards the new Entertainment trade-in-the-pocket patterns and aesthetics, made for tourists and online fandom. The change in the rules of the sport over the last 7 years or so, also is reflected in a change in how the sport is actually taught...even in spaces that feel VERY Thai. The sport is bending to the "combo" because it is signature to Western and international fighting aesthetics, and it can be taught by less skilled/experienced coaches. Fighters did not train like that, nor did they fight like that. As the sport has become deskilled the combo has taken an increasingly important role. Added to this, gyms have had to accommodate the expectations of Westerners and other non-Thais, as the weakening of the sport economically has turned almost every gym in the tourism halo towards at least a hybrid relationship to tourism...it needs to give the Westerner something they recognize and expect...and, because tourists and adventure tourist come with all sorts of investments and motivations, on different timescales, a lower common denominator works itself into the equation. Group "classes", organized drilling of groups, increased conceptualization and rationalization of techniques involving verbal correction and demonstration, even foreign coaching, these are FOR YOU changes in the sport. Sometimes these trends and aspects will only be subtly present, sometimes they will characterize the entire process. This is an elephant ride. And often it is difficult to distinguish where the elephant ends and the ride begins. Even "Fighter Training" Isn't The Process Along these lines of hunting the "authentic" training in gyms you'll run into this difficulty. You may be in a gym full of Thai fighters, even very active Thai fighters. There aren't many combos being held for. No real "group classes". A lot of Thai culture is going on, or seems to be. You are doing the work of fighters, real fighters, right there next to you. It's by Thais its for Thais and its pretty authentic...but for these things. For one, this gym if it's not a kaimuay in the more grassroots sense, all these fighters were made somewhere else. They were bought and brought into the gym, to be part of a stable. So what you likely are seeing, and doing, isn't actually how they became what they are. They are in the polishing, or add-a-level stage. The heartbeat of what made them is elsewhere. Even if you are a developed, accomplished fighter, and you too are in the "polishing" stage, you don't have what they have, which is a very different history of training, fighting and development. They are made of a different material, so to speak, and in truth that "material" is the actual "stuff" that everyone comes to Thailand looking for, that is where the "authenticity" is in their movements, vision, rhythms, stylistics. You can do all the padwork, all the clinch rounds, all the runs, all the bagwork, all the sparring, and you'll get better, in fact a LOT better...but, you'll be missing that "authentic" piece, the thing they got before they came to this gym. To add to this, if you did seek out the kaimuay that grows fighters in the principles of the sport, and their fighting circuits, these are not economically robust spaces, they are no longer teeming with fighters, and they're not focused on the tourist. They are part of a fragmenting economy of largely provincial fighting, and in which is difficult to find one's place, especially as an adult, as they are made for youth. The best you might find are hybrid spaces, kaimuay on the low ebb, which also are run by a great kru, making room for non-Thais, but even these spaces are a kind of bricolage of culture, knowledge and practice. There is no pristine location for the "authentic". "Treated Like a Thai" A layer even further down in terms of authenticity, it's not uncommon to feel that if you've stayed a lot, trained a lot, fought a lot, that you are being (more or less) "treated like a Thai". This is a big desire in the reach for "authenticity", and that experience of being "treated like a Thai" is therefore quite meaningful. But you aren't. You are still likely on an elephant ride, in a certain regard. And that's become Thailand's traditional Muay Thai is culturally founded on intense social power disparity. It is strongly hierarchized, and hierarchies vie against other hierarchies constantly in a political struggle that the Westerner, even the Thai-speaking Westerner, largely cannot see...and if they see them, they cannot care about them in the same way a Thai does and would. This is a continuous struggle for social "position" in which the Thai fighter has almost always has almost zero power. They are bound not only by contract obligation (contract), but more significantly by strong mores of social debt and shame, and the networks of hierarchy which make up gyms, community and promotion. They are in a web with constant top-down and lateral pressures, with very limited choice, you are not. You do NOT want to be treated "just like a Thai"...and honestly, you probably can't be, even if you want to be brought into the same workouts or expectations of a fighter. The reason this is important is the almost all of the motivations you have as a fighter, to become better, to win, to be acknowledged are very, very VERY different than the Thai fighter kicking the bag right next to you...and their motivations are actually the "authentic" part of Thailand's Muay Thai. Stadium Muay Thai is not the free agent professionalism that non-Thais aspire to. It is intense social stigma straining under a culture of obligation. You can do all the work, mirror it beat for beat, but you are not in the affective position of Thai fighters, and so in some sense cannot fight like them, for their alliances and values, the things which bring the strikes out, are largely invisible to the Westerner. All these things: that they've changed the rules so Westerners can win or perform well, and will enjoy watching, that they've changed the way Muay Thai is trained, that you aren't likely exposed to the actual processes that made stadium fighters who they are today, and even that you cannot experience the disempowerment, position and dignity of Thai fighters themselves, all cut off aspects of "authenticity", much sought by those that travel in earnest. This is leaving behind all those more common internet concerns like fake fights, dives, bad match making. It's in the actual fabric of the sport itself, as Westerners reach for it, and as it has turned its face toward the Westerner, making itself for the Westerner...and others. 2. The Fighters Aren't the Same The second difficulty in reaching for "authenticity" is that even if you get through all those layers. If you shun the rehearsed combo, you identify living threads of kaimuay culture and its values and ways of life as much as possible, if you fight five round trad Muay Thai fights, don't take weight advantages when you can, if you emotionally connect with the low social position of the Thai fighter, all the things, and then make it to the ring where "authentic" Muay Thai is "happening"...it's not even happening there. I mean this in this sense. Aside from the erosion and deskilling of the sport due to new promotional motivations, tourism and market pressures, Muay Thai itself has been eroding on its own within the country. The rising economic standard out of the classes of people who traditionally fought it have changed many of the motivations and commitments of the fighters themselves, and the talent pool of fighters has dramatically decreased. I'm going to throw a wild number out, but I'm just guessing in an educated way...maybe the talent pool is 10x smaller. Leaving aside that combos and entertainment aesthetics are now working their way into more or less "Thai" gym spaces, the fighters themselves just are not that good, not as developed, complex or accomplished by the time they are in Bangkok rings. Big name gyms grab up local kaimuay talent earlier and earlier (green fruit off the tree before ripe), the developmental fighter classes (informal groups within gyms) that grow the skills are seriously on the decline. A kaimuay may have had 20 fighting boys, now may have 3? Traditionally there was a stirring of the pot that was cooking a very deep stew of skills, more and more its a process just a few ingredients heated over a short time. This is to say, even if you can get all the way to the "authentic" rings, the quality and sophistication of the Muay Thai you will be facing will lack something that "authentic" dimension that characterized the freedom and expressiveness of skill of past generations. You may in fact fight a Thai who will fight quite like a farang (as far as it goes). They may end combos with a body shot, or throw endless elbows, be unable to defend well in retreat, have a muay of one or two weapons, or be limited and simplistic in the clinch. Not only is the skillset diminished, but in new generation fighters the rhythms and shapes of fighting that are "authentic" may not be there in full force. In some ways the Westerner may encounter a dim mirror of themselves. I'm writing this because this quest for authenticity is seriously meaningful. It's meaningful to us, those of the West who love Thailand's Muay Thai, and it's also meaningful to Thais as well, who have great esteem for its legacy. The only way to significantly engage in the question of authenticity is to acknowledge that it is already substantively hybridized. You and everyone else may be on elephant rides. It's only by identifying the aspects of Muay Thai that are not made for the tourist and adventure tourist, the threads of culture and practice that developed without your presence, or others like you, and nurturing with respect those aspects, that will the authentic journey begin. You may be in a very commercial gym, full of combos and group classes, but your padman probably grew up in kaimuay culture. It's in him. It's what made him. Find ways to connect to that. There are also at times "Thai gyms" (mini-kaimuay) inside commercial gyms, which operates under a different code than the gym for customers. You may be in an Entertainment fight promotion, fight in the traditional style, try to win in the traditional style, even if the ruleset doesn't favor it. Push back against what has been made for you. Learn and identity the lineages of cultural practice that have defined Muay Thai, and connect to those purposely. In a sense, if we all realize we are on elephant rides, at a certain point you have have to love and care for the elephant itself, which is the beautiful, mysterious, almost-like-us, powerful, magical creature. This is the art of Muay Thai. And even if you aren't on the best ride, you are on a mother-effin elephant. Find the culture of the elephant. Find the elephant's history among the people. Find what the elephant needs. Find what is natural to the elephant. Protect and honor the elephant. we wrote a manifest of our values here1 point
-
This is a line of reasoning I'd like to pursue, that global Capitalism is deskilling Muay Thai fighters, but changing the rules and aesthetics to breakdown complex fighting knowledge to repetitive tasks, like throwing memorized combos, in order to increase the labor force, making individual fighters less unique and more replaceable, and transfer the knowledge core to promotional and media oriented marketing. the chat gpt summary of deskilling: The argument that capitalism induces deskilling comes primarily from Marxist and critical labor theorists, particularly Harry Braverman, who expanded on this in his influential 1974 book Labor and Monopoly Capital. Here's a breakdown of the argument: What is Deskilling? Deskilling is the process by which skilled labor is replaced with less skilled or unskilled labor—often through: Technology or automation Standardization of work tasks Fragmentation of complex jobs into simpler, repetitive tasks Why Would Capitalism Encourage Deskilling? 1. Profit Maximization Capitalist firms aim to maximize profits. One way to do this is to: Replace skilled workers (who are more expensive) with less skilled workers or machines Simplify tasks so they require minimal training, which reduces labor costs 2. Managerial Control Simplifying jobs increases management’s control over the labor process: Skilled workers often have more autonomy and bargaining power Deskilling reduces workers' independence and makes them easier to supervise, replace, and discipline 3. Increased Productivity Deskilled labor allows for: Mass production techniques (think Ford’s assembly line) Faster and more consistent output Easily interchangeable workers, which supports scalability Theoretical Roots Karl Marx: Believed capitalism alienates workers from the labor process, reducing their work to mere repetitive actions Harry Braverman: Argued that capitalist development deliberately strips away workers’ skill and knowledge to concentrate power and expertise in management1 point
-
I'm not sure which video you watched but Sylvie has a whole clinch playlist Hop In Clinch Entry Getting in & Staying In Clinch Basics Seminar1 point
-
I watched Sylvie's clinch video. I think I can relate to what you're saying. I'll practice and see if I can figure how to execute it.1 point
-
No worries! If you are unsure of the hand positioning in the clinch with this move, i can try to find some or maybe take a picture of it, it is a bit difficult to explain and understand movement correctly through text.1 point
-
I'm not sure about Sylvies approach to this, and can't really relate since i ain't that short, but i might have a small tip on closing the distance relatively safely in order to use knees.. It might be a bit clumsy to explain this in text, but i'll try. Try to push your opponent away with a teep, then follow up with a jab, you don't have to hit them with the jab, this is mainly to measure distance and maybe make them shell up a bit, then close the distance with a knee feint with your left knee, use the movement as you put your left foot on the ground again, step to the right of your opponent and try to grab them. Left hand upside down behind their neck, right arm on the outside of their bicep, use your strength to push their head downwards as you would in a normal clinch. If you do this fast enough, you will have very good controll of their body and they are in a pretty vulnerable position to take left knees in the stomach. When they try to push you away, you are also in a pretty good position to follow of with a sweep with your right leg as they step back, you will have maybe a second or so to do this as they gain their composure again, and you are still in the dominant position. I don't know how much you will understand of this as it is in text, but this has worked pretty good for me against taller opponents. But it is of course not withouts it's risks, every move is possible to counter. You might want to try this in a shadowbox routine before you apply it to sparring.1 point
-
how to use head movement in Muay Thai: https://x.com/Egokind1/status/1906268431315280261 The highlight brings in general the thought that everyone has gotten spam-the-elbows happy in Thailand. This has happened quickly, and you could pretty much see the change start in real time because of COVID, beginning when they briefly banned clinch in paranoia (and with Entertainment Muay Thai). It feels like the Yodkhunpon template (which itself as an extreme outlier, and not well-esteemed in its time) got oversimplified. A lot of Muay Thai is just becoming Muay Elbow. As defense significantly erodes in Muay Thai though, the elbow is becoming a more and more effective go-to. It becomes chicken and egg. More elbows, less defense, the less defense, the more elbows are effective. The elbow may become the iconic cliche strike of Muay Thai, when at its height Muay Thai rather rarely featured elbows. They were seen as both "low" and largely ineffective.1 point
-
There is a compelling line of development in my thought, a new/different way to relate to the past which is not reactionary. More in the piece on Bergson. This joins together the psychodynamics of our personal history to even thoughts about Muay Thai's past, the relevance of the Golden Age and it's own past, a fundament of how we perceive the value and resource of the past. When we have championed the Golden Age of Muay Thai for instance a few have pushed strongly back seeing this as "nostalgic" (refusing "growth" or "modernization"), even some intelligent ones pointing out that we don't want to return to a time of repressive social structures, power-abuse, deep income disparities across the nation. All worthy ideas of critique. But what fails to come across is that the past has deposits of tremendous knowledge which was born out of the distress, just as experiences of personal trauma produce lessons and guidance, capacities. It does not mean that one should live in constant distress. It is rather that the richness of experience, the attainment of new capacities (in the past), may powerfully inform the present.1 point
-
Consider not turnover over the kick, and instead working on the classic more upright Golden Kick: You can read more about it here: https://8limbsus.com/muay-thai-thailand/golden-kick-how-to-improve-your-thai-kick The turn over aspect of the kick is often over emphasized by non-Thai krus who don't really see all the connective tissue in the Thai Kick (generally). Most of the classic kicks turn very late in the arc, because they want to keep the opponent centered, and they don't want to be out of position for more continuous offensive flow. You can see more about Karuhat's kick here: #111 The Karuhat Rosetta Stone 7 - The Secrets of the Matador (83 min) watch it here Karuhat is the most documented Golden Age legend in history, thanks to the sum of all the filming and commentary we've been able to do with him. This session though provide the key to understanding all the other sessions. And there is a very special focus on his particular Golden Kick. An alternate kicking style: #143 Takrowlek Dejrat - Master of the Low Kick (90 min) watch it here One of the great low kicking fighters of the Golden Age teaches his squared up, pressuring, Muay Beuk fight philosophy which uses an extremely fast, vertical low kicking technique that keeps the opponent exactly where you want them. This punishing style, built on defense and ring control is extremely effective, using techniques that are not often taught. Study the low kick in a way you haven't seen before.1 point
-
I think there is way too much emphasis on technique in most commercial gyms. You just don't see that in trad Muay Thai gyms. Most of it is: here are the basics, work on getting comfortable, be aware of defense, relaxation. Spar and clinch. Technique focus can do the opposite. Make you really tense, overly critical. Combos encourage you to use your eyes much less, and just bite down on offense. Just some thoughts.1 point
-
New Film Evidence on Early Modern Muay Thai History The above video edit study of the best fighter in Thailand, Samarn Dilokvilas, is taken from one of the most remarkable film records of early modern Muay Thai. This post contains various treatments & edits of the archive footage, highlighting its aspects. Previously of the early modern period we've primarily had short very clips produced for newsreel, with opponents of unknown skill, edited to present to the foreign eye something exotic and unusual (a playlist of early modern Muay Thai footage here). With newsreels we never really know how much the action has been chosen and constructed, or how distortive that may be. The colonial British regarded Siam as comparatively "uncivilized" and the few glimpses of fight footage feel like they were chosen with that view in mind. They are brief, clashing keyholes into the art, but now read almost like puppet shows for theater goers, from a far away land. There was also a Thai filmed dramatic reenactment of a fight, which for some time was taken as genuine fight footage, the earliest on record. It suffices to say that before this film, our visual evidence for how Thailand's Muay Thai (Muay Boran) in its early modern period was fought was deeply fragmented and full of artifice. You can watch the full archive footage of the Samarn vs Somphong fight for the unofficial title of Best in Thailand, from which my edits are cut (the story of this fight and who the fighters were is further below): this footage originally was published in this longer Thai Film Archive. In this case we have lengthy, if significantly edited, fight footage purporting to cover all the rounds of a fight, as well as the showcase of some bagwork, sparring fight preparation and coverage of the historical context of the fight. And, the two fighters are thought to be two of the very best in Thailand, a showdown of great magnitude. It is far more than a keyhole. We get the sense that we are watching an actual, continuous fight from 1936. It gives us insight into the relationship between Thailand's Muay Thai and Western Boxing. You can see Samarn's Western Boxing influenced bagwork in this short edit, as well as an excerpt from General Tunwakom teaching the "Buffalo Punch" of Muay Khorat, which Samarn includes in his light work: The State of Early Modern Muay Thai and British Boxing Beginning with the first decade of the 1900s Bangkok itself was undergoing powerful modernizing influences, much of which embodied by its relationship with the British Empire. Bangkok was a deeply cosmopolitan, thriving Southeast Asian city. It has been estimated that there were as many 3,000 British serving with the Siam police in 1907. The future King of Siam, HM King Vajiravudh, who would modernize the sport would spend near a decade coming of age in Britain in college and military school (he would be given the honorary rank of General in the British army in 1915 and even thought to fight for the British in WW1). Regular Boran Kard Chuek fights were held at the city pillar (and likely in many other undocumented city locations), but there was no stadium or fixed ring in the city until King Vajiravudh came to the throne and implemented Western Boxing's influence. It was a gambling sport of the people whose gloveless, violent nature would ruffle British sensibilities. At a time when colonial powers were using the excuse of beneficently civilizing peoples of Siam's bordering countries as their governance was taken control of, British sensibilities did matter. When prince Vajiravudh's father, the famed King Chulalongkorn, formalized the three regional Schools of Muay Boran (Lopburi, Khorat and Chaiya, bestowing teaching authority to tournament winners) in 1910, he was not founding these styles, but rather consolidating them up (and to some degree secularizing) them as the sport itself was likely beginning to experience change in the face of Bangkok's modernity. This was an act of preservation and commandeering. Through the religious reforms of 1902 outlawing non-Thammayut Buddhism mahanikai practices the National government had begun discouraging customary Muay Thai pedagogies within the wat, moving it away from their magical practices. Fight wicha & magical wicha were likely seen both seen as fighting techniques. The aim was to put more martially trained men under royal auspices and in rationalized contexts. By 1919 British Boxing was taught along side Muay to police and all civil servants at Sulan Kulap Collage. The modernizing, internationalizing art of Judo was also offered. King Vajiravudh, returning to Siam to eventual ascent to the throne saw British sport as key to a society's modernization and Nationalization, and Muay Boran ring fighting was to be shaped to reflect the more rationalized (rule governed, safety concerned) character of British Boxing. The first fixed roped rings in Bangkok (1921, 1923) held both British Boxing fights and Muay Thai fights. you can see a Modernization of Thailand's Muay Thai timeline here It is enough to say that in the Muay Thai of the 1920s a modernization movement was significantly modeled on and inspired by British Boxing, and much of how Muay Thai is today comes from this modernization effort a century ago. But...did this influence change how fighters actually fought in these new rings? And if so, how much? Did Muay Thai/Boran on the one hand adhere to their own characteristics which were purposely counter to Western Boxing, pushing back to maintain its own identity resisting its influence? Or were fighters synthesizing Western Boxing with Muay Boran fighting styles? Was what was happening in the ring a combination, or an uneven example of both? We have so little visual evidence its really hard to say, but this one film (which actually seems to present two fights, more on that further down) is our deepest, most substantive look into the early history of modern Muay Thai as it actually was. My own feeling has been - and I should get that in front - is that while we may prefer to think of Thailand's Muay Thai has possessing its own pure lineage, tracing lines of of styles back even hundreds of years, the true nature of Thailand's Muay Thai is that it is, and has perhaps always been an absorbing art, a synthesizing art, which has taken numerous threads of influence and experience (including international influence) and woven itself into something absolutely unique: an at least 100 year old highly optimized, deeply tested ring fighting art. And substantive to modern Muay Thai has been its dialogue with Western Boxing from its inception in the early 1900s. Not only did British Boxing and Thailand's ring Muay Thai exist side by side in Bangkok, and not only was Muay Boran remodeled on the rules and engagements of British Boxing, but the fighters themselves fought in both sports. The cross-pollination was unavoidable, and probably in some ways quite effectively pursued. The 1936 Fight For Who Was the Best in Thailand: Samarn vs Somphong The fight in question in fact is purported to be for who was the best Muay Thai fighter in Thailand. I think the record is probably a little thin on this, but Alex Tsui provides a very powerful picture of the build up to this fight. Please read his original write up which contains many more details on it here. an excerpt: It was Samarn vs. Somphong III, fought at the Pattani Municipal Government Hall, on 29 April, 1936. Samarn Dilokvilas (career 1926-52), was the grand champion of Siam, from 1933 to 1939, and in those years, he was truly invincible and widely revered as a national hero. His rival, Somphong Vejasidh (career 1930-51) was the most dangerous puncher during the same period, being unbeaten all the way until he captured the 128-pound title at Suan Sanuk arena. A showdown with Samarn was inevitable. Samarn versus Somphong, the most fabulous arch-rivalry in muaythai (then called Siamese boxing in the western media) before the Second World War, enacted a total of six encounters stretching from 1933 to 1939, each a classic in its own right, that captured nation-wide interest and media coverage, in pre-war days of Thailand. Samarn had won the first showdown, an unprecedented ten-round muaythai match at the constitution celebrations, 1933, in what was always remembered by critics as one terrific epical battle. The rematch, in early 1934, was likewise very close, and Somphong managed to clinch a draw, at Suan Sanuk. Thereafter, both went separate ways abroad to campaign in pro boxing, which was a premier spectator sport on the international scene. Samarn fought in Penang and Burma, raking up a record of 9-1, having lost once to Young Tarley, but won the rematch. His last oversea outing was a knockout victory, in four rounds, against George Goudie, lightweight champion of Burma, on 14 October, 1935. Samarn’s ring savvy was so tantalizing that the media in Penang had given him the rather adorable title “Gentleman of Siam”. Somphong’s overseas campaign was just as enviable. A 10-1 record in Singapore (Asia’s most popular boxing hub right up to the 50’s), all against proven pugilists on the international circuit speaks for itself. His last outing was a kayo over Japanese champion Yoshio Natori in four. So, when the two top fighters of the kingdom were set to meet again, for the third time, it was national news, for the question after the two bitter battles had remained to be decided – Which of the two was the best fighter in Siam? So we have two of the best Muay Thai fighters in Thailand, arch rivals, facing off after each has also been a dominant professional boxer in the Southeast Asian boxing circuit. The two fighters embody, one could say, the acme of the sport as it was in relation to its modern inception in dialogue with Western Boxing. They are Muay Thai fighters and boxers. How would they fight? The fight is a remarkable document of the relationship between Western Boxing and Muay Thai in early modern Thailand. It's boxing influence is visibly pronounced. And, there is telltale Muay Boran presence as well. In my film-study edit of the style of Sarman Dilokvilas you can see the boxing footwork, the slips, the jabs, the angle taking, but also the reverse elbows, the throws, the spins, stance switching. It is an amalgam. There are some problems with the footage that I discovered in frame by frame study. The first of course is that it isn't' continuous. It has been edited to capture the "action". And, given the rest of the archive film, and its purpose, this seems likely done by someone who wasn't particularly knowledgeable about fighting (at least by class). This to me means the cut of the film itself probably left out a great deal of the art of fighting, the distance taking, the manipulation of tempo, moments of defense or delay. It presents a very clashy fight. It may have been like that, but editing is a powerful aesthetic tool, and to properly edit a fight take a knowledgeable eye. This is to say, this footage in my view likely suffers some from the same interpretative problems as Newsreel footage. Compounding this problem, the edit itself reuses action sequences, repeating them at different times in the fight, sometimes cutting them into different rounds. I started documenting these by timestamp, but as their number grew I just left it to another day. This just adds to the artificially constructed, and perhaps mis-representational nature of the film, not something that would be immediately apparent. above an example of many repeated action sequences This being said, there is still a lot left on the bone. Lots of techniques and exchange moments. Editing these clash-like exchanges into quick repetitions and a slow motion copy (the video at the top of this post) is to help reveal both their technical nature and to capture their rhythms (removing them from the master, original film edit, whatever it's intention). It seeks to catalogue the fighting techniques of Samarn Dilokvilas, who purportedly was the best Muay Thai fighter in Thailand. How much of a window into the state of 1930's Muay Thai does this fight between Samarn Dilokvilas and Somphong Vejasidh give us? These are both fighters who moved to the professional, international boxing circuit after dominating Thailand's Muay Thai, to great acclaim (mirroring the career patterns of later World Boxing Champions Saensak in the 1970s, Samart, Samson, Weerapol in the 1980s and 90s). They fight with a boxing influence. Sarman on the bag looks like a boxer, again: Did much of Thailand's Muay Thai reflect this? Or was this pocketed knowledge. A small piece of evidence toward understanding this is also found in the archive film. There is another fight in the footage, also edited for action (also with duplicated sequence cuts). It looks like it was a pre-fight show the day before the big fight. You can see that the rope configuration is different, with only two ropes instead of three. So these fighters may very well be important Muay Thai fighters in the Pattani (southern Thailand) scene. While the Sarman vs Somphong fight edit features very little clinch or grappling, this fight as it was edited is almost completely clinch and grappling, peppered with clashing entry strikes. Clinch breaks are still very quick, there is little fighting for position, but we really don't know how much this presentation has been manipulated by the editor of the footage. He might very well have liked to produce a contrast between the two fights, aesthetically, and may have cut out a lot of the art of the fight as boring to non-fight fans. Early Modern Muay Thai and Grappling How much clinch or even grappling (with a possible Judo influence?) was in Thailand's Early Modern Muay Thai is an interesting question. A 1922 Australian news report says that while throws are permitted, clinching is not, while it is unclear how clinch. This possible prelim fight which is filled with grappling-type action is perhaps the best evidence for the role grappling played in some Muay Thai contests in this era. Here is a slow motion edit of those clash entry grappling exchanges, as well as the complete archive footage of the fight: Conclusion What we are left with are two Muay Thai fights, one that features two of the best in Thailand which is quite boxing heavy in style, and the the other a possible prelim fight that is predominately grappling and clash entries. Two very different "Muay Thais". My own suspicion is that Muay Thai in the 1920s-1940s was very eclectic. When the railroads were built in the first decades of the 1900s the diverse knowledge of provincial Muay Thai and its fighting styles were suddenly becoming more connected. Chiang Mai and Lampang fighters could much more readily fight fighters of Pattani and Nakhon si Thammart in the South, or Khorat in Issan. The melting pot of the railroads, nexus'd in Bangkok, but actually in various hubs (this significant fight was in Pattani) must have produced a great influx of new fight knowledge, with styles interacting with styles. It is notable that the symbol of modernization, the train, features prominently in the film, and there are no Thai "wais" in that footage. Everyone is shaking hands proudly in a Western manner. Modernization. If we add in that Bangkok itself, the heart of Thailand's modernization and growing Nationalism, Boxing in part a symbol this internationalizing standard, at first by the King himself and other royal elites, but then systematically within the Thai government, police and civil service. Thailand was encircled by a Southeast Asian professional boxing circuit, born of regional colonialism, in Burma, Singapore, the Philippines, and international boxing surely represented the world standard of fighting within Thailand. It was honorific for Thailand's Muay Thai fighters to succeed in the Southeast Asian circuit, and Thai fighters likely successfully boxed abroad before even the turn of the century. In thinking about the state of Thailand's Muay Thai in the 1930s we must consider these flows of people, from the provinces into Bangkok via railroad, the outward international interaction with the Southeast Asian boxing circuit, and place that Boxing held in the royal and government concept of modernization itself. At this time Muay Thai was rich, eclectic and evolving, full of cross-influences, but also likely held areas of strong resistance, local knowledge bases which preserved and hardened themselves in terms of identity. It was as true mixed martial art ecology of fighting.1 point
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
Footer title
This content can be configured within your theme settings in your ACP. You can add any HTML including images, paragraphs and lists.
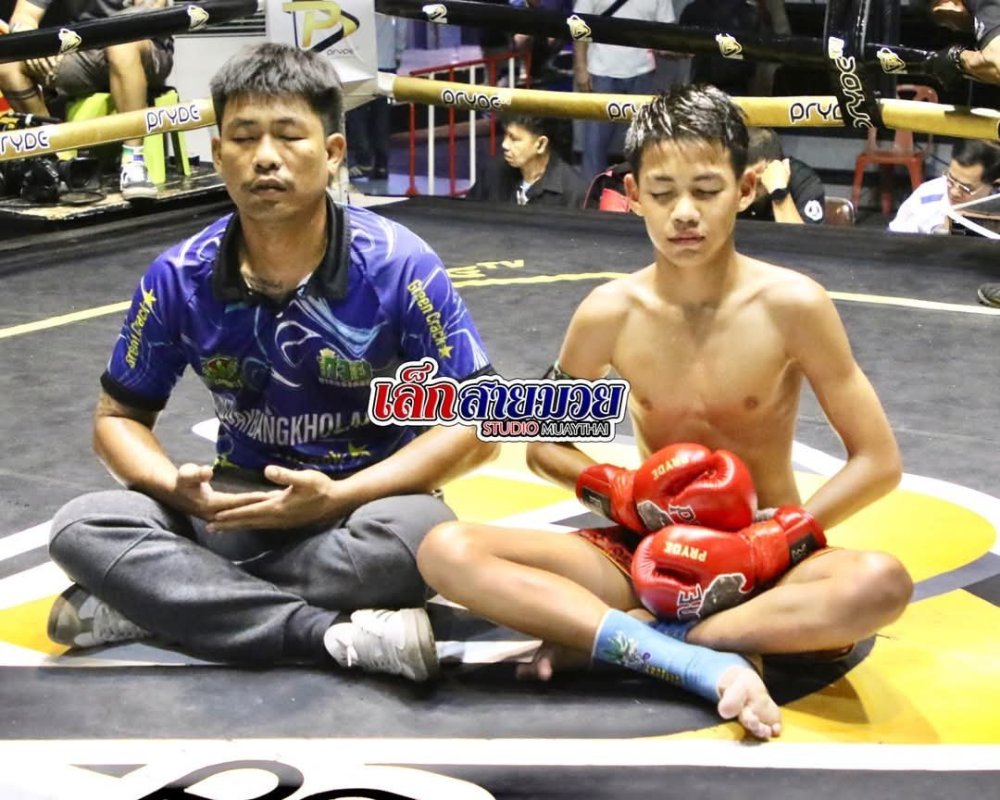
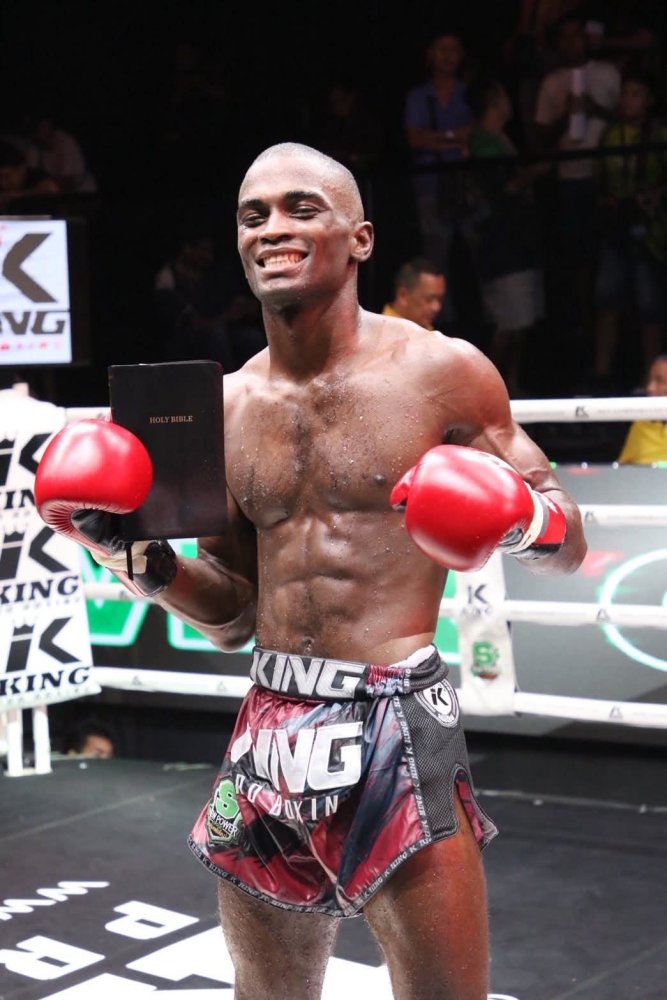












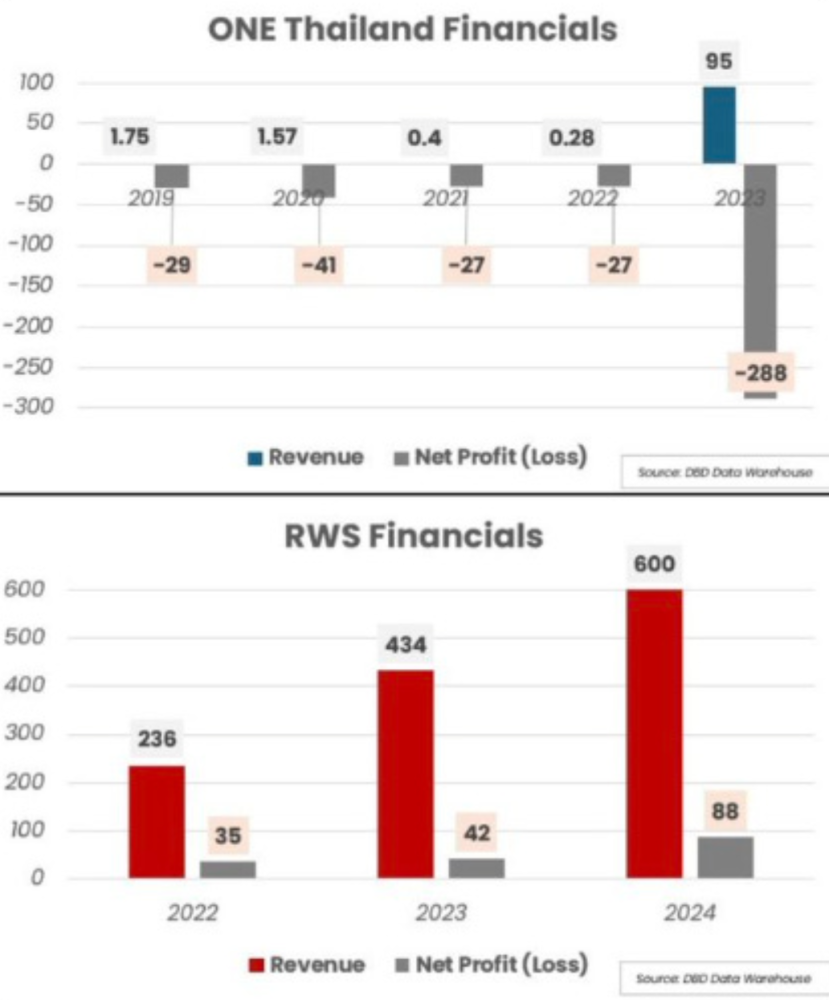


.thumb.png.13261730540de8cfcb0cb78aebad4022.png)


